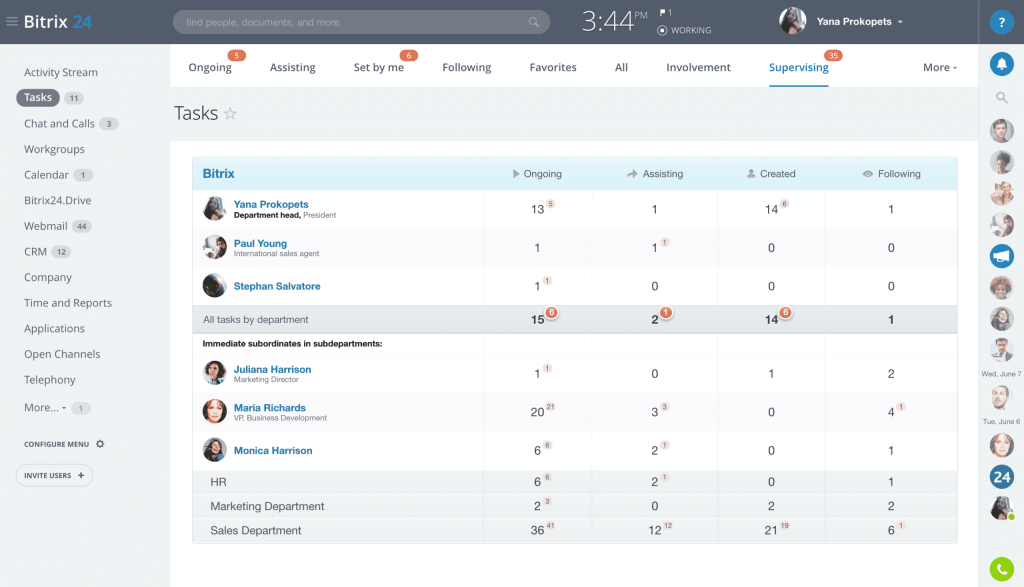
In the dynamic world of marketing, understanding your audience is paramount. Gone are the days of one-size-fits-all campaigns. Today, success hinges on personalization, relevance, and delivering the right message to the right person at the right time. This is where CRM marketing segmentation comes into play. It’s the art and science of dividing your customer base into distinct groups, or segments, based on shared characteristics. This allows you to tailor your marketing efforts, improve customer engagement, and ultimately, drive a higher return on investment (ROI).
What is CRM Marketing Segmentation?
At its core, CRM (Customer Relationship Management) marketing segmentation is the process of grouping your customers based on common traits. These traits can range from demographics and behaviors to purchase history and even psychographics. The goal is to create segments that are homogeneous within themselves (meaning the customers within a segment are similar) and heterogeneous between segments (meaning the segments are different from each other). This allows you to create highly targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups.
Think of it like this: Imagine you’re a chef. You wouldn’t prepare the same dish for everyone, would you? You’d consider their dietary restrictions, preferences, and even the occasion. CRM marketing segmentation allows you to be that chef, crafting the perfect “dish” (marketing message) for each “guest” (customer segment).
Why is CRM Marketing Segmentation Important?
In today’s competitive landscape, CRM marketing segmentation is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Here’s why:
- Improved Customer Engagement: When you send relevant messages, your customers are more likely to engage with your brand. They feel understood and valued.
- Increased ROI: Targeted campaigns are more efficient. You’re not wasting resources on reaching customers who aren’t interested in your products or services.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalized experiences lead to happier customers, increased loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Better Resource Allocation: Segmentation helps you prioritize your marketing efforts and allocate your budget effectively.
- Deeper Customer Understanding: By analyzing your segments, you gain valuable insights into your customers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Targeted campaigns are more likely to convert leads into customers and increase sales.
Key Steps in CRM Marketing Segmentation
Implementing CRM marketing segmentation effectively involves a strategic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define Your Objectives
Before you start segmenting, clarify your goals. What do you hope to achieve? Are you trying to increase sales, improve customer retention, or launch a new product? Your objectives will guide your segmentation strategy and the metrics you use to measure success.
2. Choose Your Segmentation Criteria
This is where you decide what characteristics you’ll use to divide your customer base. Common criteria include:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income, education, location, occupation.
- Psychographics: Lifestyle, values, interests, attitudes, personality traits.
- Behavioral: Purchase history, website activity, product usage, brand loyalty, engagement with marketing campaigns.
- Geographic: Country, region, city, climate.
- Firmographics (for B2B): Company size, industry, revenue, number of employees.
The best criteria to use will depend on your business and your objectives. Consider using a combination of criteria for more precise segmentation.
3. Collect Data
You’ll need data to segment your customers. Data can come from various sources, including:
- Your CRM system: This is the central hub for customer data.
- Website analytics: Track website activity and user behavior.
- Social media analytics: Gather insights into customer demographics, interests, and engagement.
- Surveys and questionnaires: Collect direct customer feedback.
- Third-party data providers: Supplement your data with external sources.
Ensure your data is accurate, up-to-date, and compliant with privacy regulations.
4. Segment Your Customers
Use your chosen criteria and data to create your segments. Aim for segments that are:
- Measurable: You can track their size and characteristics.
- Accessible: You can reach them with your marketing messages.
- Substantial: They are large enough to be profitable.
- Differentiable: They respond differently to marketing efforts.
- Actionable: You can create marketing campaigns tailored to them.
5. Develop Targeted Marketing Campaigns
Once you have your segments, it’s time to create targeted marketing campaigns. This includes:
- Crafting personalized messages: Tailor your messaging to the specific needs and interests of each segment.
- Choosing the right channels: Select the communication channels that are most effective for each segment (e.g., email, social media, SMS).
- Offering relevant products and services: Recommend products or services that align with each segment’s needs.
- Setting up automated workflows: Automate your marketing efforts to save time and improve efficiency.
6. Test and Optimize
Marketing is an iterative process. Continuously test your campaigns and analyze the results. Track key metrics such as conversion rates, click-through rates, and customer engagement. Use the data to optimize your campaigns and improve your segmentation strategy.
7. Review and Refine
Customer behavior and market trends change over time. Regularly review your segments and make adjustments as needed. This might involve updating your criteria, creating new segments, or merging existing ones. Stay flexible and adaptable.
Types of CRM Marketing Segmentation
There are various ways to segment your customers. Here are some common types:
1. Demographic Segmentation
This is one of the most common types of segmentation. It involves dividing your customers based on demographic characteristics such as age, gender, income, education, and location. For example, a clothing retailer might segment its customers by age to target different age groups with specific clothing styles.
2. Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation focuses on customers’ lifestyles, values, interests, and attitudes. This type of segmentation can provide valuable insights into what motivates your customers. For example, a company selling eco-friendly products might target customers who value sustainability and environmental responsibility.
3. Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation groups customers based on their actions, such as purchase history, website activity, and engagement with marketing campaigns. This allows you to target customers based on their actual behavior. For example, an online retailer might segment its customers based on their purchase frequency and offer exclusive discounts to frequent buyers.
4. Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides customers based on their location. This can be useful for businesses with a physical presence or those that offer location-specific products or services. For example, a restaurant might target customers within a certain radius of its location with local advertising.
5. Needs-Based Segmentation
This type of segmentation focuses on identifying the specific needs that customers are trying to fulfill. This requires understanding the problems your customers are trying to solve or the goals they are trying to achieve. For example, a software company might segment its customers based on their specific software needs, such as project management, customer support, or sales automation.
6. Value-Based Segmentation
Value-based segmentation groups customers based on their lifetime value to your business. This allows you to prioritize your marketing efforts on your most valuable customers. This can involve offering exclusive benefits, personalized service, or loyalty programs to retain your most valuable customers.
7. Purchase Stage Segmentation
This segmentation strategy considers where a customer is in the buying journey. Common stages include awareness, consideration, decision, and loyalty. Tailoring marketing messages to a customer’s stage in the buying journey ensures you’re providing the most relevant information at the right time. For instance, a customer in the “awareness” stage might benefit from educational content, while a customer in the “decision” stage might be ready for a special offer.
Tools and Technologies for CRM Marketing Segmentation
Several tools and technologies can help you with CRM marketing segmentation:
- CRM Software: Platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 provide the foundation for managing customer data and segmenting your audience. They allow you to store, organize, and analyze customer information, and they often include built-in segmentation features.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: Tools like Marketo, Pardot, and ActiveCampaign enable you to automate your marketing campaigns and personalize your messaging based on customer segments.
- Email Marketing Software: Platforms like Mailchimp, Constant Contact, and Sendinblue allow you to segment your email list and send targeted email campaigns.
- Data Analytics Tools: Tools like Google Analytics, Tableau, and Power BI can help you analyze your customer data and gain insights into your customer segments.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs like Segment and Tealium are designed to collect and unify customer data from various sources, providing a single view of each customer. This unified data can then be used for more effective segmentation and personalization.
Best Practices for CRM Marketing Segmentation
To maximize the effectiveness of your CRM marketing segmentation efforts, consider these best practices:
- Start Small: Don’t try to segment your entire customer base at once. Begin with a few key segments and gradually expand your efforts.
- Focus on Actionable Segments: Ensure that your segments are meaningful and that you can take action based on the insights you gain.
- Keep it Simple: Avoid over-segmenting your customer base. Too many segments can make it difficult to manage your campaigns and track your results.
- Use Data Wisely: Rely on accurate and up-to-date data to inform your segmentation strategy.
- Personalize Your Messaging: Tailor your messaging to the specific needs and interests of each segment.
- Test and Iterate: Continuously test your campaigns and refine your segmentation strategy based on the results.
- Respect Customer Privacy: Always comply with privacy regulations and obtain customer consent before collecting and using their data.
- Integrate Across Channels: Ensure that your segmentation strategy is integrated across all your marketing channels, including email, social media, and your website.
- Train Your Team: Educate your marketing team on the importance of segmentation and how to use it effectively.
- Measure and Track Results: Regularly track key metrics such as conversion rates, click-through rates, and customer engagement to measure the success of your segmentation efforts.
Examples of CRM Marketing Segmentation in Action
Let’s look at some real-world examples of how businesses are using CRM marketing segmentation to achieve their goals:
- E-commerce Retailer: An online clothing store segments its customers based on purchase history. They identify a segment of “high-value customers” who have made frequent purchases in the past. They send these customers exclusive early access to sales, personalized product recommendations, and special offers.
- Software Company: A software company segments its customers based on their industry and company size. They create targeted marketing campaigns for each segment, highlighting the specific features and benefits of their software that are most relevant to their needs. They might create separate landing pages and case studies for each industry.
- Subscription Service: A streaming service segments its customers based on their viewing habits. They recommend movies and TV shows based on each customer’s preferences, and they send personalized email newsletters with curated content.
- Travel Agency: A travel agency segments its customers based on their travel interests and budget. They send targeted email campaigns with vacation packages that match their preferences. They might have segments for luxury travelers, budget travelers, adventure seekers, and family travelers.
- Financial Institution: A bank segments its customers based on their financial needs and life stages. They offer tailored financial products and services, such as student loans for young adults, mortgages for homeowners, and retirement planning for seniors.
Challenges and Considerations
While CRM marketing segmentation offers significant benefits, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Data Quality: The accuracy and completeness of your data are critical to the success of your segmentation efforts. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate segments and ineffective campaigns.
- Data Privacy: You must comply with all relevant privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Transparency with customers about how you collect and use their data is essential.
- Resource Constraints: Segmentation can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially for small businesses. You may need to invest in CRM software, marketing automation tools, and data analysis resources.
- Over-Segmentation: Creating too many segments can make it difficult to manage your campaigns and track your results. Focus on creating a manageable number of actionable segments.
- Lack of Integration: If your segmentation strategy is not integrated across all your marketing channels, you may not be able to deliver a consistent and personalized customer experience.
- Measurement Challenges: Accurately measuring the ROI of your segmentation efforts can be challenging. You need to track key metrics and attribute results to specific segments.
The Future of CRM Marketing Segmentation
The future of CRM marketing segmentation is likely to be shaped by several trends:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning will play an increasingly important role in segmentation, enabling businesses to identify more complex patterns in customer data and create more sophisticated segments.
- Hyper-Personalization: As technology advances, businesses will be able to personalize their marketing messages at an even more granular level, targeting individual customers with highly tailored content and offers.
- Real-Time Segmentation: Businesses will be able to segment their customers in real-time based on their behavior and interactions, enabling them to deliver highly relevant messages at the exact moment a customer is most receptive.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Customer experience will become even more critical. Businesses will focus on creating seamless and personalized experiences across all touchpoints.
- Increased Data Privacy: The focus on data privacy will continue to increase, and businesses will need to adapt their segmentation strategies to comply with evolving regulations.
Conclusion
CRM marketing segmentation is a powerful strategy that can help you understand your customers better, improve customer engagement, and drive significant business results. By carefully defining your objectives, choosing the right segmentation criteria, collecting and analyzing data, and developing targeted marketing campaigns, you can create a more personalized and relevant customer experience. Embrace the power of segmentation, and you’ll be well on your way to building stronger customer relationships and achieving your marketing goals. Remember to continuously test, refine, and adapt your segmentation strategy to stay ahead of the curve in today’s ever-changing market. By focusing on the needs and preferences of your customers, you can create a win-win situation that benefits both your business and your customers.