Small Business CRM Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Finding the Right Fit and Saving Money
Small Business CRM Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the world of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software can feel like traversing a jungle. You’re bombarded with options, features, and most importantly, price tags. For small businesses, every penny counts. Choosing the right CRM is crucial for boosting sales, improving customer relationships, and streamlining operations. But overpaying for a system that doesn’t fit your needs is a mistake you can’t afford to make. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the intricacies of small business CRM pricing, helping you understand the costs, compare options, and ultimately, find the perfect CRM solution without breaking the bank.
Why CRM is Essential for Small Businesses
Before we delve into the pricing specifics, let’s quickly recap why a CRM is so vital for small businesses. In today’s competitive landscape, building and maintaining strong customer relationships is paramount. A CRM system acts as the central nervous system for your customer interactions, providing a 360-degree view of each customer. Here’s why it’s essential:
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM systems help you track interactions, personalize communication, and provide exceptional customer service.
- Increased Sales: By managing leads, automating sales processes, and tracking performance, CRM systems can significantly boost sales.
- Enhanced Efficiency: CRM systems automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Better Data Insights: CRM provides valuable data on customer behavior, sales trends, and marketing campaign effectiveness.
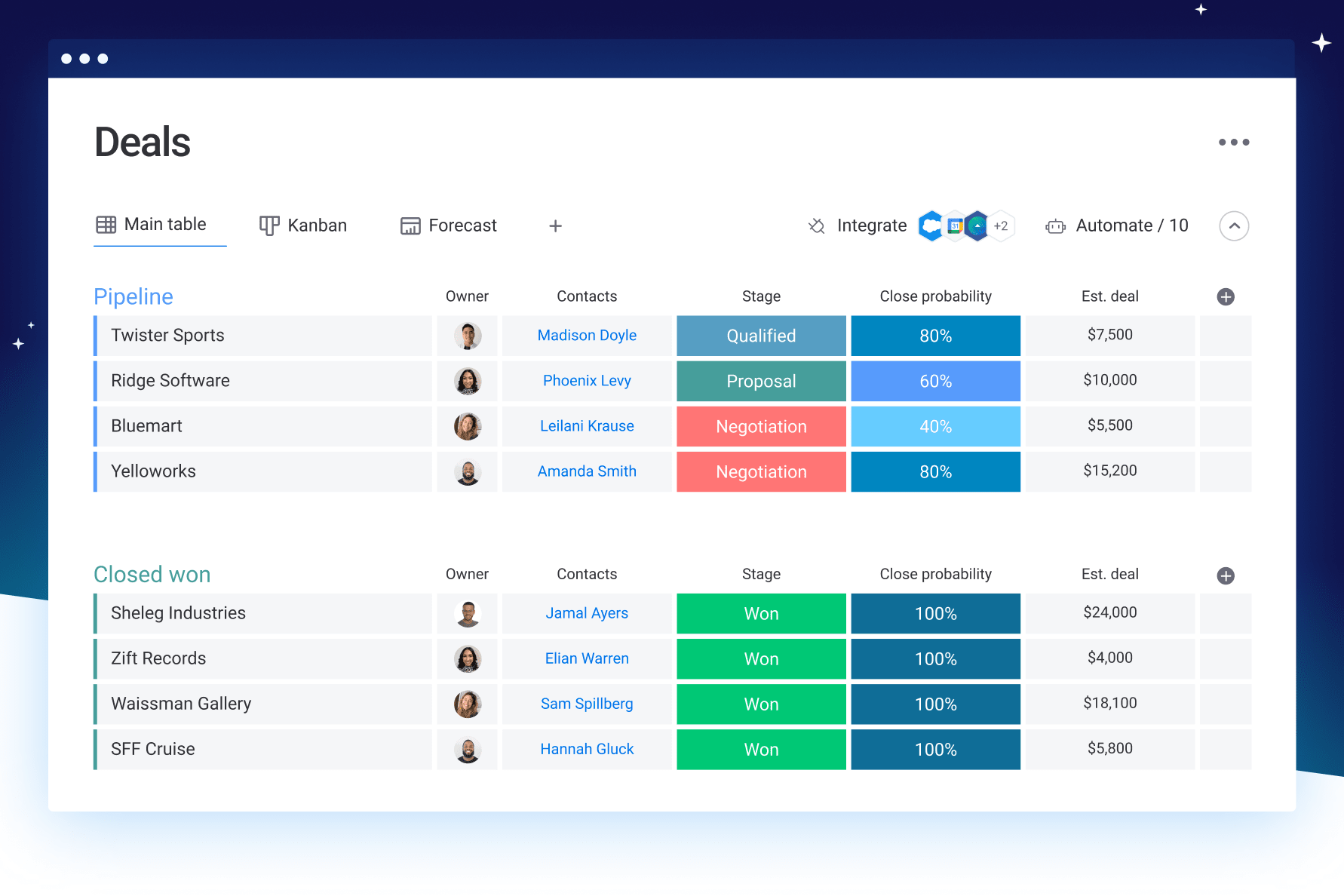
- Centralized Information: Keep all your customer data in one place, accessible to your team, eliminating the chaos of scattered spreadsheets and emails.
Understanding CRM Pricing Models
The pricing landscape for CRM software is diverse, with various models to choose from. Understanding these models is the first step towards making an informed decision. Here are the most common pricing models:
1. Per-User, Per-Month Pricing
This is the most prevalent pricing model. You pay a monthly fee for each user who has access to the CRM system. The price per user can vary significantly, depending on the features included, the vendor, and the size of your business. This model offers predictability, allowing you to easily budget for your CRM costs. However, it can become expensive as your team grows. Be mindful of whether a “user” is defined as any employee with access, or only those who actively use the system.
2. Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing often accompanies per-user pricing. Vendors offer different plans with varying features and price points. Each tier caters to a specific business size or set of needs. For instance, a basic plan might include contact management and basic sales tracking, while a premium plan offers advanced features like marketing automation, workflow automation, and integration capabilities. This model allows you to scale your CRM functionality as your business grows, but it’s crucial to carefully assess your current and future needs to choose the right tier.
3. Usage-Based Pricing
Some CRM vendors charge based on usage, such as the number of contacts stored, emails sent, or features used. This model can be cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating needs or those that don’t require extensive CRM usage. However, it can be challenging to predict costs, and overages can quickly add up. Carefully examine the usage metrics and their associated costs before committing to this model.
4. Free CRM Options
Several CRM vendors offer free versions of their software. These free plans typically have limited features and user capacity. They can be an excellent starting point for very small businesses or startups with basic CRM needs. However, as your business grows, you’ll likely need to upgrade to a paid plan to access more advanced features and accommodate more users. Remember that “free” often comes with limitations, such as storage constraints, limited customer support, and the potential for advertisements.
5. On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Pricing
While less common for small businesses due to the associated costs and complexity, some CRM systems are offered as on-premise solutions. This means you purchase a license and install the software on your own servers. On-premise solutions typically involve a significant upfront investment, including software licenses, hardware, and IT support. Cloud-based (SaaS – Software as a Service) CRM systems are hosted by the vendor and accessed via the internet. They are typically more affordable for small businesses, with lower upfront costs and easier scalability. The pricing models discussed above usually pertain to cloud-based CRM systems.
Key Factors Influencing CRM Pricing
Several factors significantly impact the cost of a CRM system. Understanding these factors will help you make a more informed decision and avoid unexpected expenses:
1. Number of Users
As mentioned earlier, the number of users is a primary driver of cost, especially with per-user pricing models. Carefully estimate the number of users who will need access to the CRM system. Consider both current and future needs. It’s often more cost-effective to start with a plan that accommodates potential growth rather than having to upgrade frequently.
2. Features and Functionality
The features you need will significantly impact the price. Basic CRM systems typically include contact management, lead management, and sales tracking. More advanced features, such as marketing automation, workflow automation, email marketing integration, and advanced reporting, come at a premium. Prioritize the features that are essential for your business and avoid paying for features you don’t need.
3. Integrations
The ability to integrate with other software and applications is crucial. If you need to integrate your CRM with your email marketing platform, accounting software, e-commerce platform, or other tools, factor in the integration costs. Some vendors offer native integrations, while others require third-party integrations, which may involve additional fees.
4. Customer Support
The level of customer support offered can vary significantly. Some vendors provide basic support, while others offer premium support with dedicated account managers, phone support, and priority assistance. Consider the level of support you need and factor in the associated costs. Good customer support can be invaluable, especially during the initial implementation phase and when troubleshooting issues.
5. Data Storage and Security
The amount of data storage you need and the security features offered can also influence the price. CRM systems store sensitive customer data, so robust security measures are essential. Ensure the vendor offers data encryption, regular backups, and compliance with relevant data privacy regulations. Consider the storage capacity you’ll need and any associated costs.
6. Training and Implementation
Implementing a CRM system requires training for your team. Some vendors offer training as part of their pricing plans, while others charge extra. Factor in the cost of training and implementation, including any consulting fees or internal resources required.
7. Contract Length and Payment Options
CRM vendors often offer discounts for longer-term contracts. Consider the contract length and payment options available. Some vendors offer monthly, quarterly, or annual payment plans. Choose the option that best suits your budget and cash flow needs.
Top CRM Systems for Small Businesses and Their Pricing
Let’s explore some of the top CRM systems for small businesses and their pricing structures. Please note that pricing can change, so always check the vendor’s website for the most up-to-date information.
1. HubSpot CRM
HubSpot is a popular CRM platform, especially known for its free CRM offering. The free version includes essential features like contact management, deal tracking, and basic email marketing. HubSpot also offers paid plans with more advanced features, including marketing automation, sales automation, and customer service tools. HubSpot’s pricing is tiered, with different plans catering to different needs and business sizes. They offer a free forever plan, which is a great starting point. Paid plans range from affordable starter plans to professional and enterprise options with a comprehensive feature set. Their pricing is generally competitive, making them a strong contender for small businesses.
- Free: Contact management, deal tracking, basic email marketing, and more.
- Starter: (Paid) Starts at a reasonable price per month, offering more features and usage limits.
- Professional: (Paid) More advanced features and higher usage limits, suitable for growing businesses.
- Enterprise: (Paid) The most comprehensive plan, designed for large businesses with complex needs.
2. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM is another widely used CRM platform, known for its affordability and extensive feature set. Zoho offers a free plan for up to three users, making it an excellent option for very small businesses or startups. Their paid plans offer a range of features, including sales force automation, marketing automation, and customer service tools. Zoho’s pricing is tiered, with different plans catering to different business sizes and needs. Zoho CRM offers a balance of features and affordability, making it a strong contender for small businesses. Zoho also provides various add-ons and integrations, allowing for customization and expansion of functionality. Their pricing is often seen as competitive in the market.
- Free: Up to 3 users, with basic CRM features.
- Standard: (Paid) A good starting point with essential features.
- Professional: (Paid) More advanced features and customization options.
- Enterprise: (Paid) The most comprehensive plan, with advanced features and high usage limits.
3. Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM designed to help sales teams manage leads and close deals. It’s known for its intuitive interface and ease of use. Pipedrive’s pricing is per-user, per-month, with different plans offering varying features and usage limits. Pipedrive is a great choice for sales-driven small businesses that want a CRM that is easy to implement and use. Pipedrive’s focus on sales makes it a good fit for companies that prioritize lead management and deal tracking. They offer a straightforward pricing structure, making it easy to understand the costs.
- Essential: (Paid) Includes core sales features.
- Advanced: (Paid) Offers more features, including automation.
- Professional: (Paid) Includes advanced features, such as revenue forecasting.
- Enterprise: (Paid) The most comprehensive plan, with advanced features and high usage limits.
4. Freshsales (Freshworks CRM)
Freshsales, now part of Freshworks CRM, is a user-friendly CRM system designed for sales teams. Freshsales offers a free plan for up to 3 users, making it an attractive option for small businesses. Their paid plans offer a range of features, including sales automation, lead scoring, and email marketing integration. Freshsales is known for its ease of use and affordable pricing. Freshsales is a great option for businesses looking for a CRM that is easy to set up and use, with a focus on sales productivity. Their pricing is competitive, and they offer a free plan, which is a good starting point for small businesses.
- Free: Up to 3 users, with basic CRM features.
- Growth: (Paid) Offers a good set of features at an affordable price.
- Pro: (Paid) More advanced features, including automation and reporting.
- Enterprise: (Paid) The most comprehensive plan, with advanced features and customization options.
5. Agile CRM
Agile CRM is a comprehensive CRM platform that offers a wide range of features, including sales, marketing, and customer service tools. Agile CRM offers a free plan for up to 10 users, making it a good option for small businesses. Their paid plans offer a range of features, including marketing automation, sales automation, and customer service tools. Agile CRM offers a good value for the money, with a wide range of features at a competitive price. It’s a good choice for businesses seeking a comprehensive CRM solution with a focus on sales, marketing, and customer service. They have a free plan that allows for a decent amount of users, making it a viable option for small teams. Their pricing is also tiered, allowing businesses to scale as they grow.
- Free: Up to 10 users, with basic CRM features.
- Starter: (Paid) A basic plan with a good set of features.
- Regular: (Paid) More advanced features and usage limits.
- Enterprise: (Paid) The most comprehensive plan with advanced features.
Tips for Negotiating CRM Pricing
Once you’ve identified the CRM systems that meet your needs, it’s time to negotiate pricing. Here are some tips to help you get the best deal:
1. Research and Compare
Before negotiating, thoroughly research the pricing of different CRM systems. Compare features, pricing models, and contract terms. This will give you leverage during negotiations.
2. Leverage Competition
Let vendors know you’re considering other options. This can often incentivize them to offer a more competitive price or additional features. Be transparent about your needs and budget, and let them know why you’re considering their competitors.
3. Negotiate Discounts
Don’t be afraid to ask for discounts. Vendors often offer discounts for longer-term contracts, bulk purchases, or upfront payments. Ask if they offer any special promotions or discounts for small businesses or startups. Inquire about the possibility of a discount based on the number of users.
4. Focus on Value
Instead of solely focusing on price, emphasize the value the CRM system brings to your business. Highlight the benefits, such as increased sales, improved customer relationships, and enhanced efficiency. This can help you justify the investment and negotiate for additional features or support.
5. Ask for a Trial Period
Before committing to a long-term contract, ask for a free trial period. This will allow you to test the CRM system and ensure it meets your needs. During the trial period, evaluate the system’s features, ease of use, and customer support. This will help you make an informed decision and avoid buyer’s remorse.
6. Consider Customization Costs
Factor in the costs of customization and integrations. If you need to customize the CRM system or integrate it with other software, ask about the associated costs. Some vendors offer customization services, while others require third-party integrations. Understand the total cost of ownership, including customization and integration costs.
7. Review the Contract Carefully
Before signing a contract, carefully review the terms and conditions. Pay attention to the pricing model, contract length, payment options, and cancellation policies. Ensure you understand all the costs and obligations. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and negotiate any terms that are unfavorable.
Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Beyond the base price of the CRM system, there can be hidden costs that can significantly impact your budget. Here are some hidden costs to watch out for:
1. Implementation Costs
Implementing a CRM system can involve costs for data migration, system configuration, and training. Some vendors offer implementation services, while others require you to handle it yourself. Factor in the cost of implementation, including any consulting fees or internal resources required.
2. Integration Costs
Integrating your CRM with other software and applications can involve additional costs. Some vendors offer native integrations, while others require third-party integrations. Factor in the cost of integrations, including any setup fees or ongoing maintenance costs.
3. Training Costs
Training your team on how to use the CRM system is essential for ensuring its success. Some vendors offer training as part of their pricing plans, while others charge extra. Factor in the cost of training, including any internal resources required.
4. Data Migration Costs
Migrating your existing customer data to the new CRM system can be time-consuming and complex. Some vendors offer data migration services, while others require you to handle it yourself. Factor in the cost of data migration, including any data cleansing or formatting required.
5. Customization Costs
If you need to customize the CRM system to meet your specific needs, factor in the customization costs. Some vendors offer customization services, while others require you to hire a third-party developer. Understand the total cost of ownership, including customization costs.
6. Add-on Costs
Some CRM systems offer add-ons or extra features that are not included in the base price. Factor in the cost of any add-ons or extra features you need. This can include additional storage, advanced reporting, or specific integrations.
7. Ongoing Maintenance Costs
CRM systems require ongoing maintenance, including software updates, security patches, and technical support. Factor in the cost of ongoing maintenance, including any subscription fees or support contracts.
Making the Right Decision for Your Small Business
Choosing the right CRM system and pricing plan is a critical decision for any small business. Here’s a summary of the key steps to take:
- Assess Your Needs: Define your business goals, identify your CRM requirements, and prioritize the features you need.
- Research and Compare: Research different CRM systems, compare their features, pricing models, and customer reviews.
- Set a Budget: Determine your budget and stick to it. Consider the total cost of ownership, including the base price, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Evaluate Pricing Models: Understand the different pricing models and choose the one that best suits your needs and budget.
- Negotiate and Ask Questions: Negotiate pricing and ask questions about the features, support, and contract terms.
- Start with a Free Trial: Take advantage of free trials to test the system and ensure it meets your requirements.
- Choose the Right Plan: Select the plan that offers the features you need at a price you can afford.
- Implement and Train: Implement the CRM system and train your team on how to use it effectively.
- Monitor and Optimize: Monitor your CRM usage and optimize your processes to maximize its value.
By following these steps, you can find the right CRM system for your small business and create a CRM strategy that contributes to your success. Remember to prioritize your needs, research thoroughly, and negotiate effectively to get the best value for your investment.
Choosing a CRM system is an investment in your business’s future. By taking the time to understand the pricing models, assess your needs, and negotiate effectively, you can find a CRM solution that empowers your team, strengthens customer relationships, and drives growth. Don’t rush the process. Take your time, do your research, and make an informed decision. The right CRM system can be a game-changer for your small business.