Boosting Your Indonesian Small Business: A Comprehensive Guide to CRM Solutions

Boosting Your Indonesian Small Business: A Comprehensive Guide to CRM Solutions
In the bustling landscape of Indonesian business, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are the engines driving economic growth. To thrive in this competitive environment, these businesses need every advantage they can get. One of the most powerful tools available is a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about CRM solutions tailored for small businesses in Indonesia, from understanding the basics to selecting the perfect system and maximizing its benefits.
What is CRM and Why Does Your Indonesian Small Business Need It?
At its core, CRM is a technology that helps businesses manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. Think of it as a centralized hub for all your customer information, from initial contact to post-sale support. For Indonesian small businesses, this translates to:
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM helps you understand your customers better, personalize interactions, and build stronger relationships. In a market where personal connections are highly valued, this is a significant advantage.
- Increased Sales: By streamlining the sales process, CRM enables your sales team to close deals faster and more efficiently. It helps identify and nurture leads, track progress, and forecast sales accurately.
- Enhanced Customer Service: CRM provides a complete view of customer interactions, allowing you to deliver faster and more effective support. Happy customers are repeat customers, and repeat customers are the lifeblood of any business.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRM collects and analyzes data, providing valuable insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and marketing effectiveness. This data empowers you to make informed decisions and optimize your business strategies.
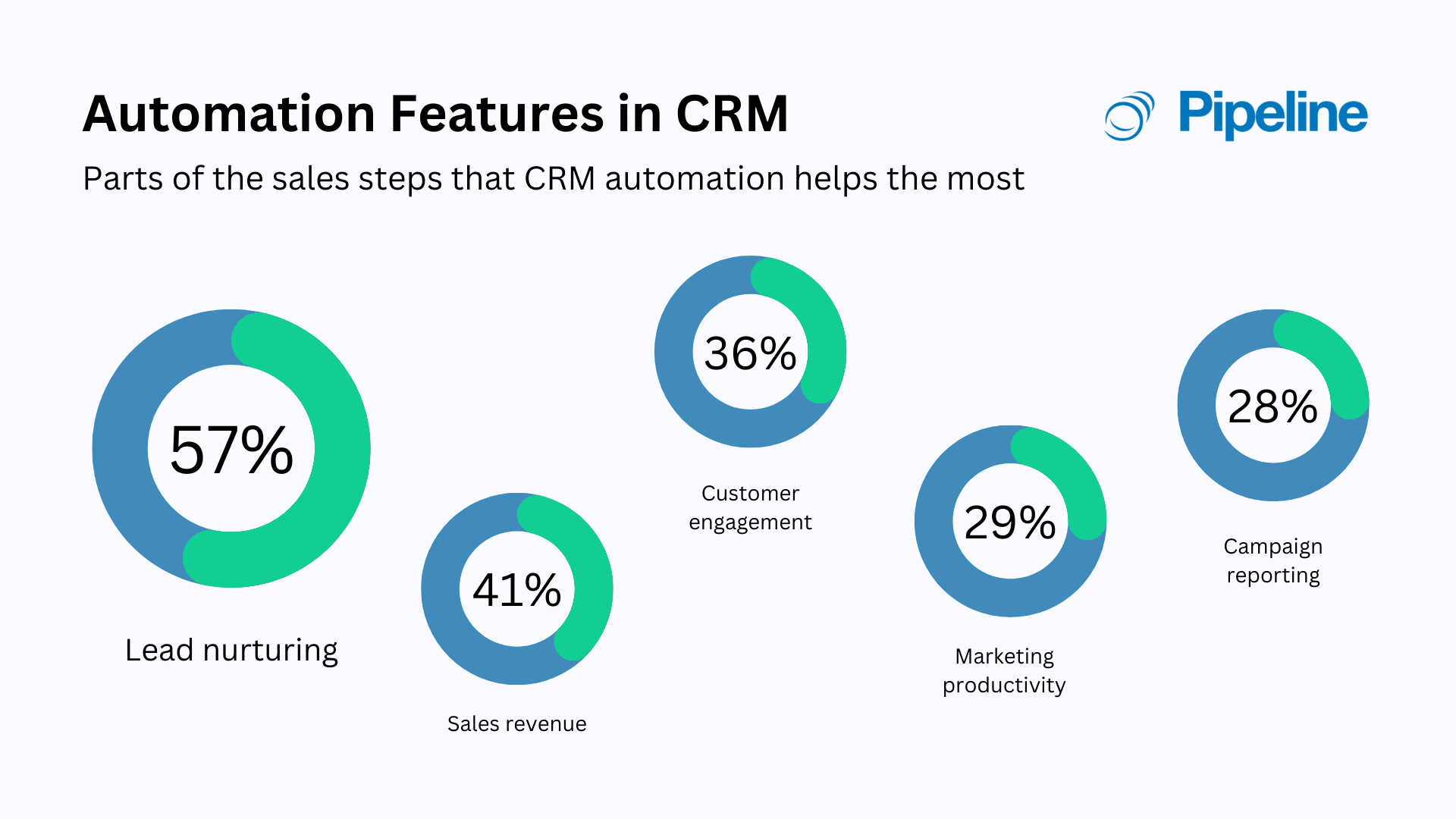
- Improved Efficiency: Automating tasks, such as data entry and follow-up emails, frees up your team to focus on more important activities, like building relationships and closing deals.
In the context of the Indonesian market, with its unique cultural nuances and rapid technological advancements, a well-implemented CRM system can be a game-changer. It allows you to:
- Adapt to Local Market Conditions: CRM helps you tailor your marketing and sales efforts to the specific needs and preferences of Indonesian customers.
- Manage Language Barriers: Many CRM systems offer multilingual support, enabling you to communicate effectively with customers in Bahasa Indonesia and other local languages.
- Leverage Mobile Technology: With the widespread use of smartphones in Indonesia, mobile CRM solutions allow your team to access customer data and manage interactions on the go.
Key Features to Look for in a CRM System for Your Indonesian Small Business
Choosing the right CRM system is crucial for its success. Here are the key features to consider:
1. Contact Management
This is the foundation of any CRM system. It allows you to store and manage all your customer contact information, including names, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles. Look for features like:
- Centralized Database: A single, organized place to store all customer information, eliminating the need for spreadsheets and scattered data.
- Contact Segmentation: The ability to categorize contacts based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchase history, and interests. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns.
- Import/Export Capabilities: The ability to easily import and export contact data from other sources, such as spreadsheets and email marketing platforms.
2. Sales Automation
This feature streamlines the sales process, saving your team time and effort. Key features include:
- Lead Management: Tracking and managing leads from initial contact to conversion. This includes lead scoring, lead nurturing, and opportunity management.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Visualizing the sales process and tracking deals through different stages, from prospecting to closing.
- Automated Tasks: Automating repetitive tasks, such as sending follow-up emails, scheduling appointments, and generating reports.
- Sales Forecasting: Predicting future sales based on historical data and current deals in the pipeline.
3. Marketing Automation
This feature helps you automate marketing tasks, such as email campaigns and social media posts. Key features include:
- Email Marketing: Creating and sending targeted email campaigns to different customer segments.
- Marketing Segmentation: Segmenting your audience based on various criteria to personalize your marketing messages.
- Social Media Integration: Connecting your CRM to your social media accounts to track engagement and manage social media campaigns.
- Landing Page Creation: Creating landing pages to capture leads and promote your products or services.
4. Customer Service and Support
This feature helps you provide excellent customer service and support. Key features include:
- Help Desk: Managing customer inquiries and support tickets.
- Knowledge Base: Creating a library of articles and FAQs to help customers find answers to their questions.
- Live Chat: Providing real-time support to customers through live chat.
- Customer Feedback: Collecting customer feedback to improve your products and services.
5. Reporting and Analytics
This feature provides insights into your business performance. Key features include:
- Sales Reports: Tracking sales performance, such as revenue, sales volume, and conversion rates.
- Marketing Reports: Tracking the performance of your marketing campaigns, such as email open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates.
- Customer Service Reports: Tracking customer service metrics, such as response times and customer satisfaction scores.
- Customizable Dashboards: Creating custom dashboards to visualize key performance indicators (KPIs).
6. Mobile Accessibility
With the increasing use of smartphones in Indonesia, having a mobile-friendly CRM is essential. This allows your team to access customer data and manage interactions on the go, improving productivity and responsiveness.
7. Integration Capabilities
Choose a CRM that integrates with other tools you already use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. This will streamline your workflow and improve data accuracy.
8. Security and Compliance
Ensure the CRM system you choose has robust security features to protect your customer data. It should also comply with relevant data privacy regulations, such as the Indonesian Personal Data Protection Law (PDP Law), which is currently being finalized.
Top CRM Systems for Indonesian Small Businesses
Several CRM systems cater specifically to the needs of small businesses in Indonesia. Here are some of the top contenders:
1. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM is a popular choice for small businesses worldwide, and it’s also well-suited for the Indonesian market. It offers a comprehensive suite of features, including contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, and customer service tools. It’s known for its user-friendly interface, affordability, and robust customization options. Zoho CRM also offers excellent integration capabilities with other Zoho apps and third-party services.
2. Hubspot CRM
HubSpot CRM is a free CRM system that’s a great option for small businesses that are just getting started. It offers a range of features, including contact management, deal tracking, and email marketing tools. HubSpot CRM is known for its ease of use and its focus on inbound marketing. It also integrates seamlessly with other HubSpot products, such as its marketing and sales hubs.
3. Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM system that’s designed to help sales teams close more deals. It offers a visual sales pipeline, deal tracking, and sales automation tools. Pipedrive is known for its simplicity and its focus on sales productivity. It’s a good choice for businesses that are looking to improve their sales process.
4. Freshsales
Freshsales is a CRM system that’s designed to help businesses manage their sales and customer support operations. It offers features such as contact management, sales automation, and live chat. Freshsales is known for its affordability and its user-friendly interface. It’s a good choice for businesses that are looking for a CRM system that can handle both sales and customer support.
5. Salesforce Essentials
Salesforce Essentials is a simplified version of the Salesforce CRM system, designed for small businesses. It offers a range of features, including contact management, sales automation, and customer service tools. Salesforce Essentials is known for its scalability and its integration capabilities. It’s a good choice for businesses that are looking for a CRM system that can grow with them.
6. Barantum CRM
Barantum CRM is a CRM system specifically designed for the Indonesian market. It offers features tailored to the local business environment, including support for Bahasa Indonesia and integration with popular local payment gateways. It’s a good choice for businesses that are looking for a CRM system that understands the Indonesian market.
7. Qontak.com
Qontak.com is another CRM provider that focuses on the Indonesian market. They offer a comprehensive solution with features like sales automation, omnichannel communication, and customer support tools. They often highlight their local support and understanding of Indonesian business practices.
Steps to Implement a CRM System for Your Indonesian Small Business
Implementing a CRM system is a significant undertaking, but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Define Your Goals and Requirements
Before you start looking at CRM systems, take the time to define your goals and requirements. What do you want to achieve with a CRM system? What features do you need? What are your budget and resources? Having a clear understanding of your needs will help you choose the right system and ensure its success.
2. Research and Evaluate CRM Systems
Once you know your goals and requirements, research different CRM systems and compare their features, pricing, and reviews. Consider the systems mentioned above and others, and create a shortlist of potential candidates. Take advantage of free trials to test the systems and see which one best fits your needs.
3. Choose the Right CRM System
Based on your research and evaluation, choose the CRM system that best meets your needs. Consider factors such as features, pricing, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
4. Plan Your Implementation
Develop a detailed implementation plan. This should include steps such as data migration, user training, and system customization. Clearly outline the roles and responsibilities of each team member.
5. Migrate Your Data
Migrate your existing customer data to the new CRM system. This may involve importing data from spreadsheets, databases, or other systems. Ensure that your data is accurate and complete.
6. Customize the System
Customize the CRM system to meet your specific needs. This may involve configuring fields, creating custom reports, and integrating the system with other tools. The goal is to have the CRM work for your business, not the other way around.
7. Train Your Team
Train your team on how to use the new CRM system. Provide them with the necessary training materials and support. Ensure that everyone understands how to use the system effectively.
8. Launch and Monitor
Launch the CRM system and monitor its performance. Track key metrics, such as sales, customer satisfaction, and efficiency. Make adjustments as needed to optimize the system.
9. Provide Ongoing Support and Training
Provide ongoing support and training to your team. CRM systems are constantly evolving, and your team will need to stay up-to-date on the latest features and updates. Regular training sessions can help them maximize their use of the system.
10. Regularly Review and Optimize
Regularly review your CRM system’s performance and make adjustments as needed. Ensure that the system is meeting your business needs and that you are getting the most out of your investment. Consider asking for feedback from your team to identify areas for improvement.
Tips for Successful CRM Implementation in Indonesia
Successfully implementing a CRM system in Indonesia requires a strategic approach. Here are some tips to help you succeed:
- Choose a System with Local Support: Select a CRM system that offers local support in Bahasa Indonesia. This will make it easier to get help and resolve any issues.
- Consider Cultural Nuances: Be mindful of cultural nuances when implementing your CRM system. For example, building strong relationships is crucial in Indonesian business culture.
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Ensure that your team receives comprehensive training on how to use the CRM system. Tailor the training to the specific needs of your team.
- Start Small and Scale Up: Don’t try to implement everything at once. Start with a few key features and gradually add more features as your team becomes more comfortable with the system.
- Focus on Data Quality: Ensure that your customer data is accurate and complete. Clean and accurate data is essential for making informed decisions.
- Get Buy-in from Your Team: Involve your team in the implementation process and get their buy-in. If your team is not on board, the CRM system will likely fail.
- Integrate with Local Payment Gateways: If you are using the CRM for e-commerce, integrate it with local payment gateways for seamless transactions.
- Prioritize Mobile Accessibility: Ensure that your CRM system is mobile-friendly, as many Indonesian users access data on their smartphones.
- Stay Updated on Regulations: Keep abreast of the latest data privacy regulations in Indonesia and ensure that your CRM system complies with them.
- Regularly Analyze and Adapt: Monitor your CRM’s performance regularly and be prepared to adapt your strategy based on the results. The business landscape is constantly evolving, and your CRM strategy needs to evolve with it.
The Benefits of CRM: Beyond the Basics
While the core benefits of CRM – improved customer relationships, increased sales, and enhanced customer service – are compelling, the advantages extend far beyond the basics. Consider these additional benefits specifically relevant for Indonesian small businesses:
- Improved Collaboration: CRM systems facilitate better collaboration between different departments, such as sales, marketing, and customer service. This leads to a more unified customer experience.
- Enhanced Communication: CRM systems provide a central hub for all customer communications, making it easier to track and manage interactions. This is especially important in a market where communication is key.
- Reduced Costs: By automating tasks and streamlining processes, CRM systems can help reduce operational costs.
- Increased Productivity: CRM systems can help your team become more productive by automating repetitive tasks and providing them with the information they need to be successful.
- Competitive Advantage: By leveraging the power of CRM, you can gain a competitive advantage over businesses that are not using CRM.
- Better Understanding of Customer Needs: CRM helps you gather more insights into customer behavior and preferences, allowing you to tailor your products and services to meet their needs.
- Improved Customer Retention: By building stronger customer relationships and providing excellent customer service, CRM can help you retain your existing customers.
Overcoming Challenges in CRM Implementation in Indonesia
While the benefits of CRM are undeniable, implementing a CRM system in Indonesia can present some challenges. Here are some common obstacles and how to overcome them:
- Resistance to Change: Some employees may be resistant to change, especially if they are used to working with manual processes. To overcome this, involve them in the implementation process, provide comprehensive training, and highlight the benefits of the new system.
- Data Migration Issues: Migrating data from existing systems can be complex and time-consuming. To overcome this, plan your data migration carefully, clean your data before migrating it, and test the data migration process thoroughly.
- Lack of Technical Expertise: Some small businesses may lack the technical expertise needed to implement and manage a CRM system. To overcome this, consider hiring a consultant or working with a CRM vendor that provides support and training.
- Budget Constraints: CRM systems can be expensive. To overcome this, choose a CRM system that fits your budget and consider starting with a free or low-cost plan.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating your CRM system with other tools can be challenging. To overcome this, choose a CRM system that integrates with the tools you already use and work with your CRM vendor to ensure a smooth integration.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Protecting customer data is crucial, and Indonesian businesses need to comply with the PDP Law. Ensure your CRM system has robust security features and complies with the relevant data privacy regulations.
The Future of CRM for Indonesian Small Businesses
The future of CRM for Indonesian small businesses is bright. As technology continues to evolve, CRM systems will become even more powerful and user-friendly. We can expect to see:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will play an increasingly important role in CRM, enabling businesses to automate tasks, personalize interactions, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM will become even more important, as more and more businesses rely on mobile devices to manage their customer relationships.
- Cloud-Based CRM: Cloud-based CRM systems will continue to grow in popularity, as they offer greater flexibility, scalability, and affordability.
- Focus on Personalization: CRM systems will become more sophisticated in their ability to personalize customer interactions.
- Integration with Social Media: CRM systems will continue to integrate with social media platforms, allowing businesses to manage their social media presence and engage with customers more effectively.
- Emphasis on Data Privacy: Data privacy will continue to be a top priority, and CRM systems will need to comply with the latest data privacy regulations.
To stay ahead of the curve, Indonesian small businesses should:
- Embrace Innovation: Be open to adopting new technologies and features.
- Invest in Training: Ensure that your team has the skills and knowledge they need to use the latest CRM technologies.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest CRM trends and best practices.
- Prioritize Customer Experience: Always put the customer first and focus on providing an exceptional customer experience.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Success in the Indonesian Market
In conclusion, a CRM system is an indispensable tool for Indonesian small businesses looking to thrive in today’s competitive market. By choosing the right CRM system, implementing it effectively, and leveraging its features, you can improve customer relationships, increase sales, enhance customer service, and make data-driven decisions. The path to success in the Indonesian market is paved with strong customer relationships, efficient operations, and a commitment to providing exceptional customer experiences. Embrace CRM, and watch your small business flourish.