Unlocking Innovation: How CRM Powers Small Business Growth and Transformation

Unlocking Innovation: How CRM Powers Small Business Growth and Transformation
In the dynamic world of small business, innovation isn’t just a buzzword; it’s the lifeblood. It’s what separates the businesses that thrive from those that merely survive. And in this landscape, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software has emerged as a pivotal tool, a catalyst for innovation, and a driver of sustainable growth. This article dives deep into how CRM systems empower small businesses to not only manage customer interactions but also to cultivate a culture of innovation, leading to increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and ultimately, greater profitability. We’ll explore the core functionalities, benefits, and strategies for leveraging CRM to fuel innovation within your small business.
The Foundation: Understanding CRM and Its Core Components
Before we delve into the innovative applications of CRM, it’s crucial to establish a solid understanding of what it is. At its heart, CRM is a technology solution designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It’s more than just a contact management system; it’s a comprehensive platform that integrates various business processes to provide a 360-degree view of your customers. This holistic perspective is the cornerstone of innovative strategies.
Key Components of a CRM System:
- Contact Management: This is the foundation, storing detailed information about your customers, including contact details, communication history, and purchase behavior.
- Sales Force Automation (SFA): Streamlines the sales process, from lead generation to deal closing. It automates tasks, manages pipelines, and provides sales teams with valuable insights.
- Marketing Automation: Enables businesses to automate marketing campaigns, personalize customer experiences, and track marketing performance.
- Customer Service and Support: Provides tools for managing customer inquiries, resolving issues, and providing excellent customer service.
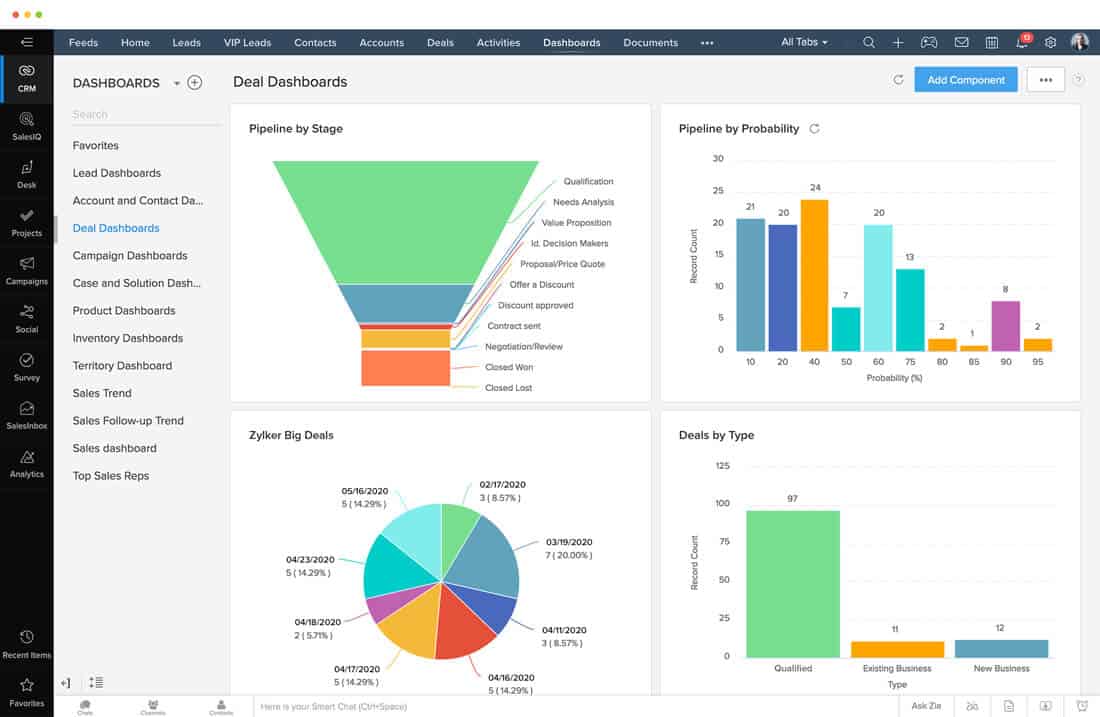
- Reporting and Analytics: Offers dashboards and reports that provide insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. This data-driven approach is critical for informed decision-making and innovation.
These components work in concert to create a centralized hub of customer information, empowering small businesses to understand their customers better, personalize interactions, and ultimately, drive innovation.
CRM as a Catalyst for Innovation: Beyond the Basics
While the core functionalities of CRM are valuable in themselves, the real power lies in how they can be leveraged to foster innovation. CRM is not just a tool for managing customer data; it’s a platform for understanding customer needs, identifying opportunities, and driving continuous improvement. It allows small businesses to move beyond reactive customer service and adopt a proactive, innovative approach.
1. Understanding Customer Needs and Preferences
CRM systems provide a goldmine of data about customer behavior, preferences, and pain points. By analyzing this data, small businesses can gain a deep understanding of their target audience. This understanding is the bedrock of innovation. It enables businesses to:
- Identify Emerging Trends: Track customer interactions, feedback, and purchase patterns to identify emerging trends and changing customer needs.
- Personalize Products and Services: Tailor products and services to meet the specific needs of individual customers, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Develop New Offerings: Use customer insights to identify gaps in the market and develop innovative products or services that address unmet needs.
2. Streamlining Processes and Improving Efficiency
CRM systems automate many repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. This increased efficiency is a key driver of innovation. By automating sales, marketing, and customer service processes, small businesses can:
- Reduce Manual Errors: Automate data entry and other manual processes to minimize errors and improve data accuracy.
- Improve Collaboration: Facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between different departments, leading to faster problem-solving and improved decision-making.
- Optimize Workflows: Streamline workflows and eliminate bottlenecks to improve overall efficiency and productivity.
3. Enhancing Customer Experience
A positive customer experience is crucial for building customer loyalty and driving repeat business. CRM systems enable small businesses to personalize interactions, provide proactive support, and resolve issues quickly and efficiently. This enhanced customer experience can lead to:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Provide personalized service and support to meet the individual needs of each customer, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
- Improved Customer Loyalty: Build stronger relationships with customers by providing exceptional service and support, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
- Positive Word-of-Mouth Marketing: Happy customers are more likely to recommend your business to others, generating positive word-of-mouth marketing and driving new business.
4. Fostering Data-Driven Decision Making
CRM systems provide valuable data and analytics that enable small businesses to make informed decisions. This data-driven approach is essential for innovation. By analyzing data from their CRM system, businesses can:
- Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitor key metrics such as sales performance, customer satisfaction, and marketing ROI to identify areas for improvement.
- Identify Growth Opportunities: Analyze sales data and customer behavior to identify new growth opportunities and market segments.
- Measure the Effectiveness of Initiatives: Track the results of marketing campaigns, sales initiatives, and customer service efforts to measure their effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
Implementing CRM for Innovation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing a CRM system is a significant undertaking, but the rewards can be substantial. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help small businesses successfully implement CRM and leverage it for innovation.
1. Define Your Objectives and Needs
Before you start looking for a CRM system, it’s essential to define your objectives and needs. What do you want to achieve with CRM? What are your key pain points? What specific features and functionalities do you need? This will help you choose the right CRM system and ensure that it meets your specific business requirements. Consider the following:
- Identify Your Goals: What are your primary goals for implementing CRM? Are you looking to increase sales, improve customer satisfaction, or streamline your marketing efforts?
- Assess Your Current Processes: Analyze your existing sales, marketing, and customer service processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Determine Your Budget: Set a realistic budget for implementing and maintaining your CRM system. Consider the cost of software, implementation, training, and ongoing support.
2. Choose the Right CRM System
There are many CRM systems available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right system is crucial for success. Consider the following factors when selecting a CRM system:
- Features and Functionality: Does the system offer the features and functionality you need? Does it support your sales, marketing, and customer service processes?
- Scalability: Can the system scale to accommodate your future growth?
- Ease of Use: Is the system easy to use and navigate? Will your employees be able to quickly learn how to use it?
- Integration Capabilities: Does the system integrate with your existing software and tools?
- Pricing and Support: Is the pricing affordable? Does the vendor offer adequate support and training?
3. Plan Your Implementation
Once you’ve chosen a CRM system, it’s time to plan your implementation. This includes data migration, system configuration, and user training. A well-planned implementation will ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions. Consider the following:
- Data Migration: Plan how you will migrate your existing customer data to the new CRM system.
- System Configuration: Configure the system to meet your specific business requirements.
- User Training: Provide adequate training to your employees so they can effectively use the CRM system.
- Timeline: Set a realistic timeline for the implementation process.
4. Implement and Test
Implement the CRM system according to your plan. Once the system is implemented, test it thoroughly to ensure that it’s working correctly and that all data is migrated accurately. This includes:
- Data Validation: Verify that all data has been migrated correctly.
- Functionality Testing: Test all features and functionalities to ensure they are working as expected.
- User Acceptance Testing: Have your employees test the system to ensure it meets their needs.
5. Train Your Team
Training your team is crucial for the success of your CRM implementation. Provide comprehensive training on how to use the system and its features. This will ensure that your employees can effectively use the CRM system and maximize its benefits. Consider the following:
- Training Materials: Provide training materials, such as user manuals, videos, and online tutorials.
- Hands-on Training: Provide hands-on training so your employees can practice using the system.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to answer questions and address any issues.
6. Monitor and Optimize
Once the CRM system is implemented, it’s essential to monitor its performance and make adjustments as needed. This includes tracking key metrics, analyzing data, and identifying areas for improvement. Consider the following:
- Track Key Metrics: Monitor key metrics, such as sales performance, customer satisfaction, and marketing ROI.
- Analyze Data: Analyze the data from your CRM system to identify trends, insights, and opportunities for improvement.
- Make Adjustments: Make adjustments to your CRM system or processes as needed to optimize its performance.
Innovation Strategies with CRM: Practical Examples
The true power of CRM lies in its ability to drive innovation. Here are some practical examples of how small businesses can leverage CRM to foster a culture of innovation:
1. Personalized Marketing Campaigns
CRM enables businesses to segment their customer base and create highly personalized marketing campaigns. This can lead to increased engagement, higher conversion rates, and improved customer loyalty. For example:
- Segmenting Customers: Divide your customer base into segments based on demographics, purchase history, and behavior.
- Personalized Messaging: Tailor your marketing messages to the specific needs and interests of each segment.
- Targeted Offers: Offer personalized promotions and discounts based on customer preferences.
2. Proactive Customer Service
CRM empowers businesses to provide proactive customer service by anticipating customer needs and resolving issues before they escalate. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and improved customer retention. For example:
- Identifying At-Risk Customers: Use CRM data to identify customers who are at risk of churn.
- Proactive Outreach: Reach out to at-risk customers to offer support and resolve any issues.
- Personalized Support: Provide personalized support based on customer history and preferences.
3. Product Development and Improvement
CRM provides valuable insights into customer needs and preferences, which can be used to inform product development and improvement. This can lead to the creation of innovative products and services that meet the needs of your target audience. For example:
- Gathering Customer Feedback: Collect customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media.
- Analyzing Customer Data: Analyze customer data to identify areas for product improvement.
- Developing New Products: Use customer insights to develop new products and services that meet unmet needs.
4. Streamlined Sales Processes
CRM can streamline sales processes, making them more efficient and effective. This can lead to increased sales and improved sales performance. For example:
- Automating Sales Tasks: Automate tasks such as lead generation, follow-up, and deal closing.
- Improving Sales Team Collaboration: Improve communication and collaboration between sales team members.
- Tracking Sales Performance: Track sales performance and identify areas for improvement.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
CRM provides valuable data and analytics that can be used to make informed decisions. This data-driven approach can lead to improved business performance. For example:
- Analyzing Sales Data: Analyze sales data to identify trends and opportunities.
- Measuring Marketing ROI: Measure the return on investment (ROI) of your marketing campaigns.
- Making Data-Driven Decisions: Use data to make informed decisions about your business strategy.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
The CRM market is vast, offering a wide range of solutions. Choosing the right one for your small business is crucial. Consider these factors:
1. Business Needs and Size
Consider the specific needs of your business. A startup will have different requirements than a company with 50 employees. Think about:
- Scalability: Choose a system that can grow with your business.
- Specific Features: Does the CRM offer the functionalities you need, such as sales automation, marketing automation, or customer service tools?
- Integration: Does it integrate with other tools you use, like email marketing platforms or accounting software?
2. Ease of Use and Implementation
The CRM should be user-friendly and easy to implement. Consider:
- User Interface: Is the interface intuitive and easy to navigate?
- Implementation Support: Does the vendor offer good support and training during implementation?
- Training Resources: Are there adequate training resources available for your team?
3. Budget
CRM systems vary in price. Consider:
- Subscription Costs: Understand the monthly or annual subscription fees.
- Implementation Costs: Factor in any costs associated with setup and data migration.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as add-ons or support fees.
4. Integration Capabilities
The CRM should integrate with your existing business tools. Consider:
- Email Marketing Platforms: Does it integrate with your email marketing software (e.g., Mailchimp, Constant Contact)?
- Social Media: Does it connect with your social media accounts?
- Accounting Software: Can it integrate with your accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero)?
5. Vendor Reputation and Support
Choose a CRM vendor with a good reputation and excellent customer support. Consider:
- Reviews and Testimonials: Research online reviews and testimonials.
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer responsive and helpful customer support?
- Updates and Maintenance: Does the vendor regularly update and maintain the system?
Real-World Examples: CRM in Action for Innovation
To truly grasp the power of CRM for innovation, let’s examine some real-world examples of how small businesses are leveraging it to achieve remarkable results.
1. A Retail Business
A small boutique retail store implemented a CRM system to personalize the shopping experience. They tracked customer purchase history, preferences, and browsing behavior. This data enabled them to:
- Personalized Recommendations: Recommend products based on past purchases and browsing history, leading to increased sales.
- Targeted Promotions: Send targeted promotions and discounts based on customer segments, such as those who had not purchased in a while or those who frequently bought certain items.
- Loyalty Programs: Implement a loyalty program that rewarded repeat customers, fostering customer loyalty and driving repeat business.
The result? A significant increase in sales, improved customer satisfaction, and a stronger brand reputation.
2. A Service-Based Business
A small consulting firm used CRM to streamline its sales process and improve customer communication. They used the CRM to:
- Manage Leads: Track leads from initial contact to closing, ensuring no leads were missed.
- Automate Follow-ups: Automate follow-up emails and reminders, freeing up the sales team to focus on building relationships.
- Improve Customer Service: Track customer interactions and provide personalized support, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
The outcome? A more efficient sales process, increased conversion rates, and improved customer retention.
3. A Software Development Company
A small software development company used CRM to gather customer feedback and improve its products. They used the CRM to:
- Collect Feedback: Collect customer feedback through surveys, support tickets, and social media.
- Prioritize Feature Requests: Prioritize feature requests based on customer demand and business goals.
- Improve Product Development: Use customer feedback to improve product development and create new features that meet customer needs.
The result? Improved product quality, increased customer satisfaction, and a competitive edge in the market.
The Future of CRM and Innovation
The future of CRM is bright, with new technologies and advancements continually emerging. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and advanced analytics are playing an increasingly important role in CRM, enabling businesses to gain even deeper insights into customer behavior and drive more effective innovation. Here’s what to expect:
1. AI-Powered CRM
AI is transforming CRM, enabling businesses to automate tasks, personalize interactions, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior. Expect to see:
- Predictive Analytics: AI-powered predictive analytics will enable businesses to anticipate customer needs and predict future behavior.
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots will provide 24/7 customer support and automate routine tasks.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI will power personalized product recommendations and marketing messages.
2. Enhanced Personalization
CRM will continue to evolve to enable even greater personalization. Expect to see:
- Hyper-Personalization: Businesses will be able to create highly personalized experiences that cater to the individual needs and preferences of each customer.
- Real-Time Personalization: Businesses will be able to personalize interactions in real-time based on customer behavior and context.
- Contextual Marketing: Marketing messages will be tailored to the customer’s current context, such as their location, device, and browsing history.
3. Increased Integration
CRM will become more integrated with other business systems, such as marketing automation platforms, e-commerce platforms, and social media platforms. Expect to see:
- Seamless Data Sharing: Data will be seamlessly shared between different systems, providing a 360-degree view of the customer.
- Automated Workflows: Workflows will be automated across different systems, improving efficiency and reducing manual errors.
- Unified Customer Experience: Businesses will be able to provide a unified customer experience across all touchpoints.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for a Future of Innovation
CRM is more than just a software solution; it’s a strategic tool that empowers small businesses to unlock innovation, drive growth, and achieve sustainable success. By understanding the core components of CRM, implementing it effectively, and embracing a data-driven approach, small businesses can transform their customer relationships into a competitive advantage. From personalizing marketing campaigns to streamlining sales processes and providing exceptional customer service, CRM offers a wealth of opportunities to innovate and stay ahead of the competition.
The journey to innovation with CRM is a continuous process of learning, adapting, and optimizing. By embracing the power of CRM and staying abreast of the latest trends and technologies, small businesses can build a future where innovation is not just a goal, but a fundamental part of their DNA. The future of business is customer-centric, and CRM is the key to unlocking that future.