Small Business CRM Implementation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Boosting Your Business

Small Business CRM Implementation: Your Roadmap to Success
Starting a small business is a thrilling adventure. You’re the captain of your own ship, navigating the vast ocean of the market. But as your business grows, so does the complexity of managing your customers, leads, and sales. This is where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes into play. Implementing a CRM can feel like a daunting task, but it’s an investment that can significantly boost your small business’s efficiency, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, your bottom line. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the entire process, from understanding the ‘why’ to the ‘how’ of CRM implementation, ensuring a smooth and successful transition.
Why Does Your Small Business Need a CRM?
Before diving into the ‘how,’ let’s explore the ‘why.’ Why should your small business consider implementing a CRM? The answer is multifaceted, but it boils down to these key benefits:
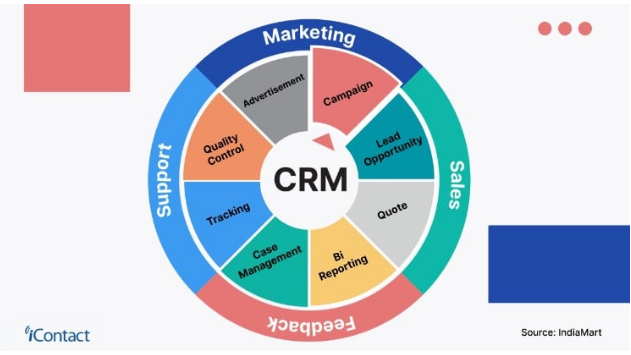
- Improved Customer Relationships: At its core, a CRM helps you build stronger relationships with your customers. It centralizes all customer data, including contact information, purchase history, communication logs, and preferences. This unified view allows you to personalize interactions, anticipate customer needs, and provide exceptional service.
- Increased Sales: A CRM streamlines your sales process. It helps you track leads, manage the sales pipeline, automate tasks, and identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling. By optimizing your sales efforts, you can close more deals and increase revenue.
- Enhanced Efficiency: A CRM automates repetitive tasks, such as data entry, email marketing, and appointment scheduling. This frees up your team’s time, allowing them to focus on more strategic activities, such as building relationships and closing deals.
- Better Data Analysis: A CRM provides valuable insights into your business performance. You can track key metrics, such as sales revenue, customer acquisition cost, and customer lifetime value. This data-driven approach allows you to make informed decisions and optimize your business strategies.
- Improved Collaboration: A CRM facilitates collaboration among your team members. All customer data is accessible to authorized users, ensuring everyone is on the same page. This improves communication, reduces errors, and enhances teamwork.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
The CRM landscape is vast, with numerous options available. Choosing the right one for your small business is crucial for success. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Your Business Needs: Before you start evaluating CRM systems, define your specific needs and requirements. What are your primary goals for implementing a CRM? What features are essential for your business? What are your current pain points that a CRM can solve?
- Scalability: Choose a CRM that can grow with your business. As your business expands, your CRM needs will evolve. Make sure the CRM you choose can accommodate your future growth.
- Ease of Use: The CRM should be user-friendly and easy to learn. A complex or clunky system can hinder adoption and productivity. Look for a CRM with an intuitive interface and clear navigation.
- Integration Capabilities: Consider the integration capabilities of the CRM. Does it integrate with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels? Integration can streamline your workflow and improve data accuracy.
- Pricing: CRM pricing varies widely. Consider your budget and choose a CRM that offers a pricing plan that fits your needs. Some CRM systems offer free plans for a limited number of users or features.
- Customer Support: Choose a CRM provider that offers excellent customer support. You’ll need assistance during implementation and ongoing use. Check the provider’s support channels, such as phone, email, and online documentation.
- Popular CRM Options for Small Businesses:
- HubSpot CRM: A popular and free CRM for small businesses, offering a range of features, including contact management, sales pipeline tracking, and email marketing.
- Zoho CRM: A feature-rich and affordable CRM with a focus on sales automation and customer service.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A leading CRM platform with a wide range of features, suitable for businesses of all sizes. However, it can be more complex and expensive than other options.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM with a visual pipeline and a user-friendly interface.
- Freshsales: A sales CRM with built-in features like phone, email, and chat.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing a CRM
Once you’ve chosen the right CRM for your small business, it’s time to implement it. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Define Your Goals and Objectives: Before you begin, clearly define your goals and objectives for implementing the CRM. What do you want to achieve? What are your key performance indicators (KPIs)? This will help you measure the success of your CRM implementation.
- Data Migration: Transferring your existing customer data into the new CRM system is a critical step. Clean and organize your data before migration to ensure accuracy. Consider the format of your data. Most CRM systems offer import tools to help you upload data from spreadsheets or other sources.
- Customize Your CRM: Tailor the CRM to your specific business needs. Configure the system’s settings, customize fields, and create workflows to automate tasks. This will ensure that the CRM aligns with your business processes.
- Train Your Team: Provide comprehensive training to your team on how to use the CRM. This is essential for successful adoption. Offer training sessions, create user guides, and provide ongoing support.
- Test the System: Before you fully launch the CRM, test it thoroughly. This will help you identify and fix any bugs or issues. Make sure the system works as expected.
- Go Live: Once you’ve tested the system and trained your team, it’s time to go live. Roll out the CRM to your entire team and start using it to manage your customer relationships.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the performance of your CRM and evaluate its effectiveness. Track your KPIs and identify areas for improvement. Make adjustments as needed to optimize your CRM usage.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to your team. Answer their questions, address their concerns, and offer additional training as needed. This will ensure that your team continues to use the CRM effectively.
Data Migration: The Foundation of Your CRM
Data migration is often the most time-consuming and potentially challenging aspect of CRM implementation. It involves transferring your existing customer data from various sources (spreadsheets, legacy systems, etc.) into your new CRM. Proper data migration is crucial for ensuring data accuracy and completeness. Here’s a more in-depth look at the process:
- Data Audit and Assessment: Before you begin migrating data, conduct a thorough audit of your existing data sources. Identify the data fields, data quality, and any potential issues. Assess the volume of data and the complexity of the migration.
- Data Cleaning and Standardization: Clean and standardize your data to ensure accuracy and consistency. This involves removing duplicates, correcting errors, and formatting data fields consistently. Use data cleaning tools or manually cleanse your data.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in your new CRM. This ensures that the data is transferred correctly. Create a data mapping document to guide the migration process.
- Data Migration Tools: Utilize the data migration tools provided by your CRM or third-party data migration tools. These tools can automate the migration process and reduce the risk of errors.
- Data Validation and Testing: After the data migration, validate the data to ensure that it has been migrated correctly. Test the system to verify that the data is accessible and functioning as expected.
- Ongoing Data Management: Implement processes for ongoing data management, including data entry, data updates, and data backups. This will ensure that your data remains accurate and up-to-date.
Customization and Configuration: Tailoring Your CRM
Once your data is migrated, it’s time to customize and configure your CRM to align with your specific business processes. This involves tailoring the system to your unique needs and workflows. Here are some key areas of customization:
- Field Customization: Customize the fields within your CRM to capture the information that is most relevant to your business. Add custom fields to track specific data points that are not included in the standard CRM fields.
- Workflow Automation: Create workflows to automate repetitive tasks, such as lead assignment, email marketing, and task creation. Automate tasks to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort.
- User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and permissions to control access to data and features within the CRM. This ensures that users can only access the information they need and that sensitive data is protected.
- Reporting and Dashboards: Customize reports and dashboards to track key metrics and gain insights into your business performance. Configure reports to display the data that is most important to your business.
- Integration with Other Systems: Integrate your CRM with other systems, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels. Integration streamlines your workflow and improves data accuracy.
Training and Adoption: Empowering Your Team
Successful CRM implementation hinges on user adoption. Your team needs to understand how to use the CRM effectively and embrace it as a valuable tool. Here’s how to ensure successful training and adoption:
- Develop a Training Plan: Create a comprehensive training plan that covers all aspects of the CRM. Tailor the training to the different user roles within your organization.
- Provide Hands-on Training: Offer hands-on training sessions that allow users to practice using the CRM. Use real-world examples and scenarios to make the training more relevant.
- Create User Guides and Documentation: Develop user guides and documentation that provide step-by-step instructions on how to use the CRM. Make the documentation easily accessible to users.
- Offer Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to your team. Answer their questions, address their concerns, and offer additional training as needed.
- Promote CRM Benefits: Communicate the benefits of using the CRM to your team. Explain how it can help them improve their performance and achieve their goals.
- Encourage User Feedback: Encourage user feedback and incorporate their suggestions into the CRM. This will help improve user satisfaction and adoption.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a CRM can present several challenges. Being aware of these challenges and having strategies to overcome them will increase your chances of success:
- Lack of User Adoption: One of the biggest challenges is getting your team to adopt the CRM. Address this by providing comprehensive training, promoting the benefits of the CRM, and offering ongoing support.
- Data Migration Issues: Data migration can be complex and time-consuming. Plan and prepare thoroughly for data migration. Clean and standardize your data before migration.
- Integration Difficulties: Integrating the CRM with other systems can be challenging. Choose a CRM that offers robust integration capabilities. Work with the CRM provider to ensure successful integration.
- Cost Overruns: CRM implementation can be more expensive than anticipated. Carefully consider your budget and choose a CRM that fits your needs. Plan for potential cost overruns and have contingency plans.
- Lack of Clear Goals: Without clear goals, it’s difficult to measure the success of your CRM implementation. Define your goals and objectives before you begin. Track your KPIs and evaluate your progress regularly.
- Poor Data Quality: Poor data quality can undermine the effectiveness of your CRM. Implement processes for data cleaning and standardization. Monitor data quality regularly.
Measuring Success: Tracking Your CRM ROI
Once your CRM is up and running, it’s essential to measure its success. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluating your return on investment (ROI). Here’s how to measure success:
- Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Identify the KPIs that are most relevant to your business goals. Examples include sales revenue, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and customer satisfaction.
- Track Your KPIs: Track your KPIs regularly. Use the CRM’s reporting features or create custom reports to monitor your progress.
- Analyze Your Data: Analyze your data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. Use the data to make informed decisions and optimize your business strategies.
- Calculate Your ROI: Calculate your ROI by comparing the costs of implementing and maintaining the CRM with the benefits it provides. This will help you justify your investment and demonstrate the value of the CRM.
- Make Adjustments: Make adjustments to your CRM usage and strategies based on your data analysis. Continuously optimize your CRM to maximize its effectiveness.
Staying Up-to-Date: Continuous Improvement
CRM implementation is not a one-time event; it is an ongoing process. To maximize the value of your CRM, you must continuously improve your usage and stay up-to-date with the latest trends and features. Here are some tips for continuous improvement:
- Review and Refine Your Processes: Regularly review your business processes and identify areas for improvement. Adjust your CRM configuration and workflows to optimize your processes.
- Stay Informed About New Features: Stay informed about the latest features and updates in your CRM. Take advantage of new features to improve your CRM usage.
- Seek Feedback from Your Team: Seek feedback from your team and incorporate their suggestions into the CRM. This will improve user satisfaction and adoption.
- Attend Training and Webinars: Attend training sessions and webinars to learn about best practices and new features. Stay up-to-date with the latest trends in CRM.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Benchmark your CRM usage against your competitors. Identify areas where you can improve and learn from their best practices.
- Regularly Evaluate Your CRM: Regularly evaluate your CRM to ensure that it is meeting your needs. Make adjustments as needed to optimize your CRM usage.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Small Business Growth
Implementing a CRM system is a pivotal step for any small business aiming for sustainable growth. While the initial setup might seem complex, the long-term benefits – improved customer relationships, increased sales, enhanced efficiency, and better data analysis – far outweigh the effort. By carefully planning your implementation, choosing the right CRM, and providing adequate training and support, you can unlock the full potential of a CRM to propel your small business to new heights. Remember to continuously monitor your performance, make adjustments as needed, and stay abreast of the latest CRM trends to ensure your success. Embrace the power of a CRM, and watch your small business flourish!