Introduction: The Power of Data-Driven CRM Marketing
In the dynamic world of marketing, relying on intuition alone is no longer sufficient. Today’s successful marketers harness the power of data to understand their customers, optimize campaigns, and drive revenue growth. At the heart of this data-driven approach lies Customer Relationship Management (CRM) marketing. CRM marketing involves using CRM systems to manage customer interactions, personalize marketing efforts, and build lasting relationships. But how do you know if your CRM marketing strategies are truly effective? The answer lies in carefully tracking and analyzing key CRM marketing metrics.
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of CRM marketing metrics, providing you with a roadmap to measure, analyze, and improve your marketing performance. We’ll explore the most critical metrics, explain how to calculate them, and offer actionable insights on how to leverage these metrics to achieve your marketing goals. Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or just starting out, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to unlock the full potential of your CRM marketing efforts.
Understanding the Importance of CRM Marketing Metrics
Before we dive into specific metrics, let’s clarify why they are so crucial. CRM marketing metrics provide a quantitative lens through which you can view your marketing performance. They offer the following benefits:
- Performance Measurement: Metrics allow you to measure the success of your marketing campaigns and initiatives.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By analyzing metrics, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation, campaign optimization, and future strategies.
- Customer Understanding: Metrics reveal valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs.
- ROI Justification: Metrics help you demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) of your CRM marketing activities to stakeholders.
- Continuous Improvement: By tracking metrics over time, you can identify areas for improvement and refine your strategies for better results.
In essence, CRM marketing metrics are the compass that guides your marketing efforts, ensuring you’re heading in the right direction and making the most of your resources.
Key CRM Marketing Metrics to Track
Now, let’s explore the most important CRM marketing metrics you should be tracking. These metrics can be broadly categorized into several areas, including:
- Customer Acquisition Metrics
- Customer Engagement Metrics
- Customer Retention Metrics
- Sales Performance Metrics
- Marketing Campaign Metrics
We’ll break down each category and discuss the specific metrics within, along with their calculations and significance.
1. Customer Acquisition Metrics
Customer acquisition metrics focus on how effectively you’re attracting new customers to your business. These metrics are crucial for understanding the efficiency of your lead generation and conversion processes.
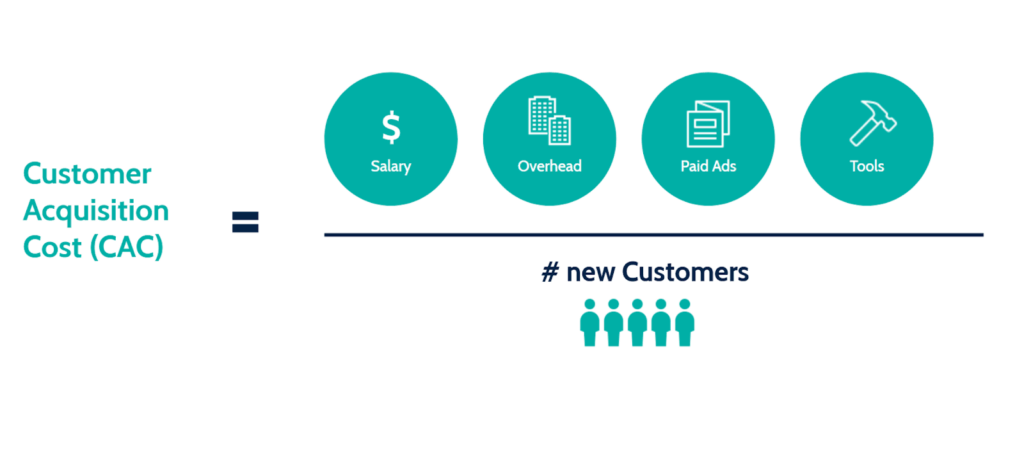
a) Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Definition: The total cost of acquiring a new customer.
Calculation: (Total Marketing and Sales Expenses) / (Number of New Customers Acquired)
Significance: CAC is a fundamental metric that helps you understand the cost-effectiveness of your customer acquisition efforts. A high CAC can indicate inefficiencies in your marketing and sales processes. A low CAC, on the other hand, signifies that you are acquiring customers efficiently.
Example: If you spend $10,000 on marketing and sales and acquire 100 new customers, your CAC is $100.
b) Conversion Rate
Definition: The percentage of leads that convert into customers.
Calculation: (Number of Customers Acquired) / (Number of Leads) * 100
Significance: Conversion rate measures the effectiveness of your sales funnel. A high conversion rate indicates that your lead nurturing and sales processes are successful. A low conversion rate suggests that there may be bottlenecks in your funnel, requiring optimization.
Example: If you have 1,000 leads and convert 50 of them into customers, your conversion rate is 5%.
c) Lead Generation Cost
Definition: The cost of generating a single lead.
Calculation: (Total Marketing Expenses for Lead Generation) / (Number of Leads Generated)
Significance: This metric helps you assess the efficiency of your lead generation campaigns. It allows you to identify the most cost-effective channels for attracting potential customers.
Example: If you spend $2,000 on a content marketing campaign and generate 200 leads, your lead generation cost is $10 per lead.
2. Customer Engagement Metrics
Customer engagement metrics gauge how actively your customers interact with your brand and marketing communications. These metrics are vital for understanding customer interest and building relationships.
a) Email Open Rate
Definition: The percentage of emails that are opened by recipients.
Calculation: (Number of Emails Opened) / (Number of Emails Delivered) * 100
Significance: Email open rate reflects the effectiveness of your email subject lines and the relevance of your content. A high open rate indicates that your emails are capturing the attention of your audience.
Example: If you send an email to 1,000 subscribers and 200 open it, your open rate is 20%.
b) Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Definition: The percentage of email recipients who click on a link within the email.
Calculation: (Number of Clicks) / (Number of Emails Delivered) * 100
Significance: CTR measures the effectiveness of your email content and calls to action. A high CTR suggests that your content is engaging and that your calls to action are compelling.
Example: If you send an email to 1,000 subscribers and 50 click on a link, your CTR is 5%.
c) Website Engagement Metrics (e.g., Time on Page, Bounce Rate)
Definition: These metrics track how users interact with your website after clicking on a link from your email or other marketing channels.
Calculation & Significance:
- Time on Page: Measures how long visitors spend on a specific page, indicating content engagement.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page, which can indicate a lack of engagement or poor user experience.
Significance: These metrics provide insights into the quality of your website content and the user experience. High time on page and a low bounce rate are generally desirable.
3. Customer Retention Metrics
Customer retention metrics measure your ability to keep existing customers engaged and loyal. Retaining customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones.
a) Customer Retention Rate (CRR)
Definition: The percentage of customers who remain customers over a specific period.
Calculation: [(Number of Customers at the End of Period – Number of New Customers Acquired During Period) / Number of Customers at the Beginning of Period] * 100
Significance: CRR is a key indicator of customer loyalty and satisfaction. A high CRR indicates that you are successfully retaining your customers. A low CRR suggests that you may need to improve your customer service, product quality, or overall customer experience.
Example: If you started the year with 100 customers, acquired 10 new customers, and ended the year with 95 customers, your CRR is 85%.
b) Customer Churn Rate
Definition: The percentage of customers who stop doing business with you over a specific period.
Calculation: (Number of Customers Lost During Period) / (Number of Customers at the Beginning of Period) * 100
Significance: Churn rate is the opposite of retention rate. A high churn rate indicates that you are losing customers at a rapid pace. Identifying the reasons for churn is crucial for addressing the underlying issues.
Example: If you started the year with 100 customers and lost 15, your churn rate is 15%.
c) Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Definition: The predicted revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with your business.
Calculation: (Average Purchase Value) * (Average Purchase Frequency) * (Average Customer Lifespan)
Significance: CLTV is a powerful metric that helps you understand the long-term value of your customers. It allows you to prioritize customer retention efforts and make informed decisions about customer acquisition spending.
Example: If a customer spends an average of $100 per purchase, makes a purchase every month (12 times a year), and remains a customer for 5 years, their CLTV is $6,000.
4. Sales Performance Metrics
Sales performance metrics focus on the effectiveness of your sales team and the overall sales process.
a) Sales Conversion Rate
Definition: The percentage of leads or opportunities that convert into sales.
Calculation: (Number of Sales) / (Number of Leads or Opportunities) * 100
Significance: This metric assesses the efficiency of your sales process. A high sales conversion rate indicates that your sales team is effectively closing deals.
Example: If your sales team has 100 opportunities and closes 20 deals, your sales conversion rate is 20%.
b) Average Deal Size
Definition: The average value of a closed deal.
Calculation: (Total Revenue from Closed Deals) / (Number of Closed Deals)
Significance: Average deal size helps you understand the value of each sale. Increasing the average deal size can significantly boost your revenue.
Example: If your total revenue from closed deals is $100,000 and you closed 50 deals, your average deal size is $2,000.
c) Sales Cycle Length
Definition: The average time it takes to close a deal.
Calculation: (Total Time for All Deals) / (Number of Closed Deals)
Significance: A shorter sales cycle is generally more efficient. Analyzing sales cycle length can help you identify bottlenecks in your sales process.
Example: If it takes an average of 30 days to close a deal, your sales cycle length is 30 days.
5. Marketing Campaign Metrics
Marketing campaign metrics provide insights into the performance of specific marketing campaigns and initiatives.
a) Return on Investment (ROI)
Definition: The profitability of a marketing campaign.
Calculation: [(Revenue Generated from Campaign – Cost of Campaign) / Cost of Campaign] * 100
Significance: ROI is a crucial metric for evaluating the effectiveness of your marketing investments. A positive ROI indicates that the campaign is profitable. A negative ROI indicates that the campaign is losing money.
Example: If a campaign generates $20,000 in revenue and costs $10,000, the ROI is 100%.
b) Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
Definition: The cost of acquiring a customer through a specific marketing campaign.
Calculation: (Total Cost of Campaign) / (Number of Customers Acquired from Campaign)
Significance: CPA helps you assess the efficiency of your marketing campaigns in acquiring new customers. A lower CPA indicates a more cost-effective campaign.
Example: If a campaign costs $5,000 and acquires 50 customers, the CPA is $100.
c) Website Traffic Sources
Definition: Tracking where your website traffic is coming from (e.g., organic search, social media, email, paid advertising).
Significance: Understanding your traffic sources helps you identify which marketing channels are most effective at driving traffic to your website. This information informs your channel allocation strategy and where to invest resources.
How to Track and Analyze CRM Marketing Metrics
Tracking and analyzing CRM marketing metrics is an ongoing process that requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before you start tracking any metrics, clearly define your marketing goals and objectives. What do you want to achieve with your CRM marketing efforts? Are you aiming to increase customer acquisition, improve customer retention, or boost sales? Your goals will determine which metrics are most relevant to track.
2. Choose the Right Metrics
Select the metrics that align with your goals and objectives. Focus on the metrics that will provide the most valuable insights into your marketing performance. Don’t try to track everything at once; start with a few key metrics and expand as needed.
3. Implement Tracking Tools
Utilize CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and analytics tools to track your metrics. Most CRM systems provide built-in reporting capabilities, and you can integrate them with other tools like Google Analytics for more comprehensive data analysis. Ensure the tools you select are capable of collecting the data you need.
4. Establish a Reporting Schedule
Set up a regular reporting schedule to monitor your metrics consistently. This could be weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on your needs. Consistent reporting allows you to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement over time.
5. Analyze the Data
Once you have collected your data, analyze it to identify trends, patterns, and insights. Look for areas where your performance is strong and areas where you can improve. Compare your results to your goals and objectives to assess your progress.
6. Take Action and Optimize
Based on your analysis, take action to optimize your CRM marketing strategies. This might involve adjusting your targeting, refining your content, improving your sales processes, or reallocating your resources. Continuously test and experiment to find what works best.
7. Review and Refine
Regularly review your metrics and reporting processes. Are you tracking the right metrics? Are your reporting schedules and tools effective? Refine your approach as needed to ensure you’re getting the most value from your data.
Tools for Tracking CRM Marketing Metrics
Several tools can help you track and analyze your CRM marketing metrics:
- CRM Systems: Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, Microsoft Dynamics 365. These systems often have built-in reporting and analytics features.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: Marketo, Pardot, ActiveCampaign, Mailchimp. These platforms provide detailed campaign performance data.
- Web Analytics Tools: Google Analytics. Essential for tracking website traffic, engagement, and conversion metrics.
- Data Visualization Tools: Tableau, Power BI. Useful for creating dashboards and visualizing your data.
- Spreadsheets: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets. Can be used for basic data analysis and reporting.
Choosing the right tools depends on your budget, technical expertise, and the complexity of your marketing operations. Many CRM and marketing automation platforms offer free or affordable options for small businesses.
Best Practices for CRM Marketing Metrics
To maximize the value of your CRM marketing metrics, follow these best practices:
- Focus on Actionable Metrics: Track metrics that provide insights you can use to improve your marketing performance. Avoid vanity metrics that don’t offer meaningful value.
- Set Benchmarks and Targets: Establish benchmarks and targets for your metrics. This provides a baseline for measuring your progress and identifying areas for improvement.
- Segment Your Data: Segment your data by customer demographics, behavior, and other relevant factors. This allows you to gain deeper insights into your customers and personalize your marketing efforts.
- Automate Reporting: Automate your reporting processes to save time and ensure consistency. Most CRM and marketing automation platforms offer automated reporting features.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Regularly review your metrics and reporting processes. Adjust your approach as needed to ensure you’re getting the most value from your data. Marketing is a dynamic field, so your measurement strategy should evolve to stay relevant.
- Integrate Data Sources: Connect your CRM with your marketing automation platform and other relevant tools to create a holistic view of your customer data. This integration allows for a more accurate and comprehensive analysis.
- Focus on Customer Lifetime Value: Prioritize metrics that contribute to long-term customer value, such as customer retention rate and CLTV. Building lasting relationships is a key ingredient for sustained success.
- Train Your Team: Ensure your marketing and sales teams understand the importance of CRM marketing metrics and how to interpret them. Provide training and resources to help them effectively utilize the data.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While tracking CRM marketing metrics is essential, it’s also easy to make mistakes that can hinder your efforts. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Tracking Too Many Metrics: Overwhelmed by data? Don’t try to track everything at once. Focus on the most critical metrics first and then expand as needed.
- Ignoring Data: Collecting data is only half the battle. Make sure you regularly analyze your data and take action on the insights you gain.
- Not Setting Goals: Without clear goals and objectives, you won’t know what to measure or how to measure success.
- Lack of Integration: Failing to integrate your CRM with other tools can lead to incomplete data and inaccurate analysis.
- Not Adapting: The marketing landscape is constantly evolving. Don’t be afraid to adapt your metrics and strategies as needed.
- Focusing Only on Short-Term Results: While short-term results are important, don’t neglect long-term metrics like CLTV and customer retention.
- Relying on Gut Feelings: Make decisions based on data, not just intuition. Data provides a more objective and reliable basis for decision-making.
Conclusion: The Path to CRM Marketing Success
In conclusion, mastering CRM marketing metrics is crucial for achieving marketing success in today’s competitive landscape. By understanding the key metrics, implementing effective tracking and analysis processes, and following best practices, you can unlock the full potential of your CRM marketing efforts.
Remember that CRM marketing is an iterative process. Continuously monitor your metrics, analyze your results, and refine your strategies to achieve your goals. By embracing a data-driven approach, you can build stronger customer relationships, drive revenue growth, and achieve sustainable success.
So, take the first step today. Define your goals, choose the right metrics, and start tracking your performance. The data is waiting to guide you to greater marketing success.