CRM Marketing Segmentation: The Ultimate Guide to Personalized Customer Experiences
CRM Marketing Segmentation: The Ultimate Guide to Personalized Customer Experiences
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, understanding your customers is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. And at the heart of understanding your customers lies one powerful strategy: CRM marketing segmentation. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the world of segmentation, exploring its definition, benefits, strategies, and practical applications. Get ready to transform your marketing efforts and create truly personalized customer experiences.
What is CRM Marketing Segmentation?
CRM marketing segmentation is the process of dividing your customer base into distinct groups (segments) based on shared characteristics. These characteristics can include demographics, behaviors, psychographics, purchase history, and more. The goal? To tailor your marketing messages, offers, and experiences to resonate with each specific segment, ultimately driving engagement, conversions, and customer loyalty.
Think of it like this: you wouldn’t give everyone the same gift for their birthday. You’d consider their individual preferences, needs, and interests. CRM marketing segmentation allows you to do the same for your customers. Instead of blasting generic messages, you create targeted campaigns that speak directly to the specific needs and desires of each segment.
The Benefits of CRM Marketing Segmentation
Why bother with segmentation? The benefits are numerous and far-reaching:
- Increased Relevance: By tailoring your messages, you ensure they’re relevant to each segment, making your marketing more impactful.
- Higher Engagement: Relevant content leads to higher engagement rates. Customers are more likely to interact with messages that speak directly to them.
- Improved Conversion Rates: Targeted offers and messaging are more likely to convert leads into customers and customers into repeat buyers.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: Personalized experiences build stronger relationships with customers, fostering loyalty and advocacy.
- Reduced Marketing Costs: By focusing your efforts on the most promising segments, you can optimize your marketing spend and reduce wasted resources.
- Better ROI: All of the above benefits contribute to a higher return on investment (ROI) for your marketing efforts.
- Deeper Customer Understanding: The process of segmentation forces you to learn more about your customers, leading to valuable insights.
Key Segmentation Strategies
There are various ways to segment your customer base. The best approach depends on your business, your target audience, and the data you have available. Here are some of the most common and effective segmentation strategies:
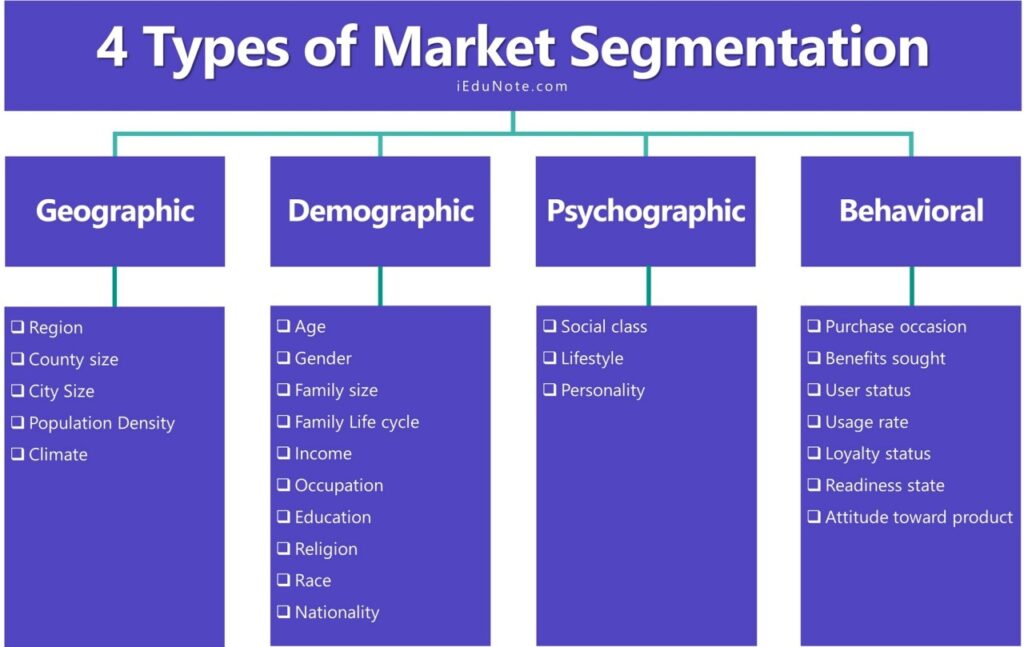
1. Demographic Segmentation
This is one of the most basic and widely used segmentation strategies. It involves dividing your customer base based on demographic factors such as:
- Age: Different age groups have different needs, preferences, and spending habits.
- Gender: Marketing messages often need to be tailored to resonate with specific genders.
- Income: Income levels can significantly impact purchasing power and product preferences.
- Education: Educational background can influence interests and purchasing decisions.
- Occupation: Different occupations have different needs and priorities.
- Marital Status: Marital status can influence lifestyle and spending habits.
- Family Size: Family size can impact purchasing decisions, especially for products related to the home and children.
Example: A luxury car manufacturer might segment its audience based on income and occupation, targeting high-income professionals with premium vehicles.
2. Geographic Segmentation
This strategy involves segmenting customers based on their geographic location. This can include:
- Country: Different countries have different cultures, languages, and regulations.
- Region: Within a country, regional differences can influence preferences and needs.
- City: Urban, suburban, and rural areas have distinct characteristics.
- Climate: Climate can impact product demand and marketing messaging.
Example: A clothing retailer might tailor its marketing messages to reflect the climate of a specific region, promoting winter coats in colder areas and swimwear in warmer areas.
3. Behavioral Segmentation
This strategy focuses on customer behavior, such as:
- Purchase History: What products or services have they purchased in the past?
- Frequency of Purchases: How often do they make purchases?
- Average Order Value: How much do they typically spend?
- Customer Loyalty: Are they repeat customers?
- Website Activity: What pages do they visit? What products do they browse?
- Engagement with Marketing Campaigns: Do they open emails? Click on links?
Example: An online bookstore might segment its customers based on their purchase history, recommending books in genres they’ve previously enjoyed.
4. Psychographic Segmentation
This strategy delves into the psychological aspects of your customers, including:
- Lifestyle: What are their hobbies, interests, and activities?
- Values: What are their core beliefs and principles?
- Attitudes: What are their opinions and perspectives on various issues?
- Personality Traits: Are they introverted or extroverted? Adventurous or cautious?
Example: A travel agency might segment its audience based on lifestyle, targeting adventure seekers with exotic trips and luxury travelers with upscale resorts.
5. Needs-Based Segmentation
This strategy focuses on the specific needs and wants of your customers, such as:
- Problem-Solving: What problems are they trying to solve?
- Desired Benefits: What benefits are they seeking from your products or services?
- Usage Rate: How often do they use your products or services?
Example: A software company might segment its audience based on their needs, targeting small businesses with affordable solutions and large enterprises with enterprise-level software.
6. Value-Based Segmentation
This strategy involves segmenting customers based on their customer lifetime value (CLTV). This involves:
- Revenue Generated: How much revenue have they generated for your business?
- Profitability: Are they profitable customers?
- Retention Rate: How likely are they to remain customers?
Example: A subscription service might segment its customers based on their CLTV, offering exclusive perks to high-value customers to retain them.
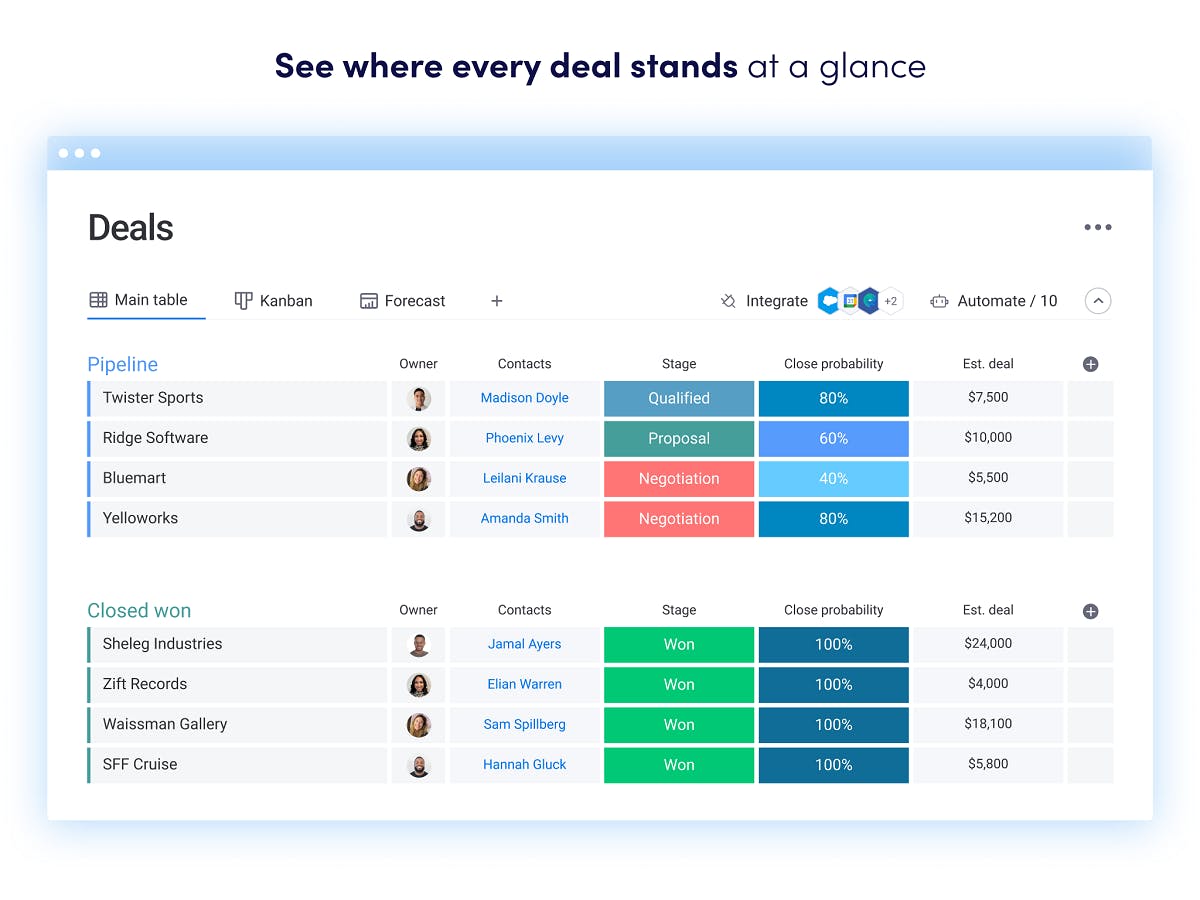
How to Implement CRM Marketing Segmentation
Implementing CRM marketing segmentation isn’t just about choosing a strategy; it’s about a systematic process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define Your Objectives
What do you hope to achieve with segmentation? Increased sales? Improved customer loyalty? Reduced marketing costs? Clearly defining your objectives will guide your segmentation strategy.
2. Collect Data
Gather as much data as possible about your customers. This can include data from your CRM, website analytics, social media, surveys, and third-party data providers. The more data you have, the more accurate your segmentation will be.
3. Choose Your Segmentation Criteria
Select the segmentation strategies that are most relevant to your business and your objectives. Consider the data you have available and the insights you hope to gain.
4. Segment Your Customer Base
Divide your customer base into distinct segments based on the criteria you’ve chosen. Use your CRM and other tools to analyze your data and identify meaningful segments.
5. Develop Targeted Marketing Campaigns
Create marketing campaigns tailored to each segment. This includes crafting specific messaging, offers, and content that resonate with each segment’s needs and preferences.
6. Implement and Test Your Campaigns
Launch your targeted campaigns and track their performance. Use A/B testing to optimize your messaging and offers for each segment.
7. Analyze Results and Refine Your Segmentation
Regularly analyze the results of your campaigns and make adjustments as needed. Customer behavior and preferences change over time, so it’s important to continuously refine your segmentation strategy.
Tools for CRM Marketing Segmentation
Several tools can help you implement CRM marketing segmentation effectively:
- CRM Software: Your CRM is the central hub for your customer data. Popular options include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: These platforms automate your marketing campaigns and allow you to personalize your messaging. Examples include Marketo, Pardot, and ActiveCampaign.
- Email Marketing Software: Email marketing software allows you to segment your email list and send targeted email campaigns. Popular options include Mailchimp, Constant Contact, and ConvertKit.
- Analytics Tools: Tools like Google Analytics provide valuable insights into customer behavior on your website.
- Data Enrichment Tools: These tools help you gather additional data about your customers, such as demographics and interests.
Best Practices for CRM Marketing Segmentation
To maximize the effectiveness of your CRM marketing segmentation, keep these best practices in mind:
- Start Small: Don’t try to segment your entire customer base at once. Start with a few key segments and gradually expand your efforts.
- Focus on Actionable Segments: Choose segments that are meaningful and allow you to create targeted campaigns.
- Keep it Simple: Avoid over-segmenting your customer base. Too many segments can be difficult to manage and can dilute your efforts.
- Be Data-Driven: Base your segmentation decisions on data, not assumptions.
- Personalize, Personalize, Personalize: The more personalized your messaging, the more effective it will be.
- Test and Optimize: Continuously test and optimize your campaigns to improve their performance.
- Be Ethical: Always respect your customers’ privacy and adhere to data privacy regulations.
- Integrate Your Systems: Ensure your CRM, marketing automation platform, and other tools are integrated to streamline your segmentation efforts.
- Monitor and Adapt: Customer behavior changes. Regularly monitor your segments and be prepared to adapt your strategy as needed.
- Train Your Team: Ensure your marketing team understands the principles of segmentation and how to implement it effectively.
Examples of CRM Marketing Segmentation in Action
Let’s look at some real-world examples of how businesses are using CRM marketing segmentation:
Example 1: E-commerce Retailer
- Segmentation Strategy: Behavioral (purchase history, website activity)
- Segments:
- High-Value Customers: Customers who have made frequent purchases and have a high average order value.
- New Customers: Customers who have recently made their first purchase.
- Browsers: Customers who have viewed products but haven’t made a purchase.
- Lapsed Customers: Customers who haven’t made a purchase in a while.
- Targeted Campaigns:
- High-Value Customers: Exclusive discounts, early access to new products, and personalized recommendations.
- New Customers: Welcome emails, introductory offers, and product tutorials.
- Browsers: Retargeting ads, abandoned cart emails, and product recommendations.
- Lapsed Customers: Re-engagement emails with special offers and promotions.
Example 2: SaaS Company
- Segmentation Strategy: Demographic (company size, industry) and Behavioral (product usage)
- Segments:
- Small Businesses: Companies with a small number of employees.
- Enterprise Clients: Large companies with a significant number of employees.
- Active Users: Customers who regularly use the product.
- Inactive Users: Customers who haven’t used the product recently.
- Targeted Campaigns:
- Small Businesses: Affordable pricing plans, onboarding assistance, and feature recommendations.
- Enterprise Clients: Custom pricing, dedicated support, and advanced features.
- Active Users: Product updates, new feature announcements, and usage tips.
- Inactive Users: Re-engagement emails with product highlights and tutorials.
Example 3: Financial Services Provider
- Segmentation Strategy: Demographic (income, age) and Needs-Based (financial goals)
- Segments:
- Young Professionals: Individuals in their 20s and 30s, focused on saving and investing.
- Retirees: Individuals nearing or in retirement, focused on retirement planning.
- High-Net-Worth Individuals: Individuals with significant assets, focused on wealth management.
- Targeted Campaigns:
- Young Professionals: Educational content on saving and investing, retirement planning tools.
- Retirees: Retirement planning services, estate planning resources.
- High-Net-Worth Individuals: Personalized financial advice, investment management services.
Challenges of CRM Marketing Segmentation
While CRM marketing segmentation offers numerous benefits, it’s not without its challenges:
- Data Quality: The accuracy of your segmentation depends on the quality of your data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed segmentation.
- Data Privacy: Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, require businesses to be transparent about how they collect and use customer data.
- Data Silos: If your customer data is scattered across different systems, it can be difficult to get a complete view of your customers.
- Resource Constraints: Implementing and maintaining a segmentation strategy can require significant resources, including time, money, and personnel.
- Complexity: Over-segmenting your customer base can make it difficult to manage your marketing efforts.
- Resistance to Change: Some team members may be resistant to adopting new segmentation strategies.
The Future of CRM Marketing Segmentation
CRM marketing segmentation is constantly evolving. Here are some trends to watch:
- AI-Powered Segmentation: Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in segmentation, automating the process of identifying segments and personalizing marketing messages.
- Hyper-Personalization: Businesses are moving towards hyper-personalization, tailoring their marketing messages to individual customers rather than broad segments.
- Real-Time Segmentation: Businesses are using real-time data to segment customers and deliver personalized experiences in the moment.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Segmentation is becoming more focused on improving the overall customer experience, rather than just driving sales.
- Emphasis on Privacy: With increasing data privacy concerns, businesses are focusing on using customer data responsibly and ethically.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Segmentation
CRM marketing segmentation is a powerful strategy for transforming your marketing efforts and creating truly personalized customer experiences. By understanding your customers, tailoring your messages, and delivering relevant content, you can drive engagement, conversions, and customer loyalty. While it requires effort and resources, the benefits of segmentation are undeniable. Embrace the power of segmentation and unlock the full potential of your CRM marketing strategy. Start small, experiment, and continuously refine your approach to achieve the best results. The future of marketing is personalized, and CRM marketing segmentation is the key to unlocking it.