Unlock Growth: The Ultimate Guide to CRM for Small Retail Businesses
Running a small retail business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling inventory, managing staff, curating the perfect product selection, and, of course, trying to attract and retain customers. In this fast-paced environment, it’s easy for customer relationships to fall by the wayside. That’s where Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come in. CRM isn’t just for the big guys with sprawling sales teams anymore. For small retail businesses, a CRM can be a game-changer, helping you streamline operations, boost sales, and build lasting customer loyalty.
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the world of CRM, specifically tailored for the unique needs of small retail businesses. We’ll explore what CRM is, why it’s essential, the benefits it offers, how to choose the right system, and practical tips for successful implementation. Get ready to transform your customer interactions and propel your business to new heights.
What is CRM and Why Does Your Small Retail Business Need It?
At its core, a CRM system is a technology that helps businesses manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. Think of it as a central hub for all things customer-related. It’s a place to store contact information, track interactions, monitor purchase history, and gain valuable insights into customer behavior. For a small retail business, this can be incredibly powerful.
In the past, small businesses often relied on spreadsheets, sticky notes, and a good memory to keep track of their customers. This approach is inefficient, prone to errors, and severely limits your ability to personalize the customer experience. With a CRM, you can:
- Centralize Customer Data: No more scattered information. All customer details, purchase history, and communication records are stored in one accessible location.
- Improve Customer Service: Access customer information instantly, allowing you to provide personalized support and address issues quickly.
- Automate Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks like sending follow-up emails, scheduling appointments, and sending promotional offers.
- Gain Valuable Insights: Analyze customer data to understand their preferences, buying habits, and overall satisfaction levels.
- Increase Sales: Identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities, personalize marketing campaigns, and nurture leads.
In essence, a CRM empowers you to build stronger relationships with your customers, leading to increased loyalty and, ultimately, higher profits. It’s about moving beyond simply selling products and creating a truly customer-centric business.
Key Benefits of Implementing a CRM for Small Retail Businesses
The benefits of implementing a CRM system are far-reaching, impacting various aspects of your small retail business. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
Enhanced Customer Relationships
This is arguably the most significant benefit. A CRM allows you to build deeper, more meaningful relationships with your customers. By understanding their needs, preferences, and purchase history, you can personalize their experience and make them feel valued. This leads to:
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Happy customers are repeat customers. A CRM helps you foster loyalty by providing exceptional service and personalized attention.
- Improved Customer Retention: Retaining existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. A CRM helps you identify and address potential issues before customers churn.
- Word-of-Mouth Marketing: Satisfied customers are more likely to recommend your business to others, generating valuable word-of-mouth referrals.
Improved Sales and Marketing Effectiveness
A CRM provides the tools you need to streamline your sales and marketing efforts, leading to better results. You can:
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: Segment your customer base and create highly targeted marketing campaigns based on their interests and buying behavior.
- Personalized Offers: Send personalized offers and promotions that resonate with individual customers, increasing the likelihood of a purchase.
- Lead Management: Track leads, nurture them through the sales funnel, and convert them into paying customers.
- Sales Performance Tracking: Monitor your sales team’s performance, identify areas for improvement, and optimize your sales strategies.
Streamlined Operations and Increased Efficiency
CRM systems automate many time-consuming tasks, freeing up your time to focus on more strategic activities. This can lead to:
- Automated Tasks: Automate tasks such as sending thank-you emails, scheduling appointments, and following up on leads.
- Centralized Data: Access all customer information in one place, eliminating the need to search through multiple systems.
- Improved Communication: Facilitate seamless communication between different departments, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Reduced Errors: Minimize manual data entry and reduce the risk of errors.
Data-Driven Decision Making
A CRM provides valuable insights into your customer base, allowing you to make informed decisions. You can:
- Track Key Metrics: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and conversion rates.
- Identify Trends: Analyze customer data to identify trends and patterns in buying behavior.
- Optimize Your Strategies: Use data insights to optimize your sales, marketing, and customer service strategies.
- Improve Forecasting: Make more accurate sales forecasts based on historical data and customer behavior.
Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Retail Business
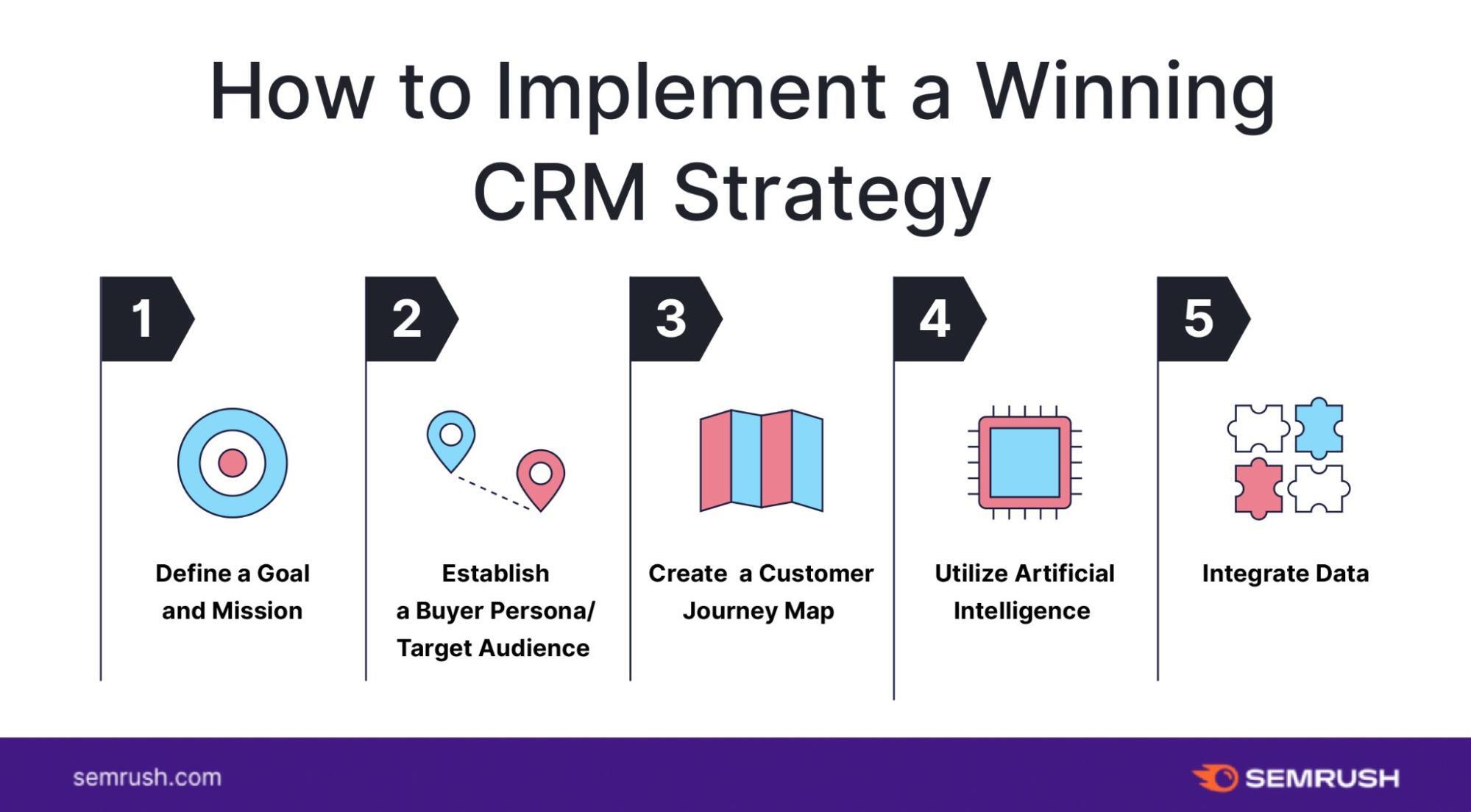
Choosing the right CRM is crucial for its successful implementation and adoption. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you select the perfect system for your needs:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start evaluating different CRM systems, take the time to define your specific needs and goals. Ask yourself:
- What are your current pain points? What challenges are you facing in managing customer relationships?
- What are your specific objectives? What do you hope to achieve with a CRM? (e.g., increase sales, improve customer service, streamline operations)
- What features are essential? What features are non-negotiable? (e.g., contact management, sales tracking, marketing automation)
- Who will be using the CRM? Consider the needs of your sales team, customer service representatives, and marketing team.
By clearly defining your needs and goals, you can narrow down your options and focus on systems that are a good fit for your business.
2. Research Different CRM Systems
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, it’s time to research different CRM systems. There are numerous options available, ranging from simple, affordable solutions to more complex, feature-rich platforms. Consider the following factors:
- Features: Does the system offer the features you need, such as contact management, sales tracking, marketing automation, and reporting?
- Ease of Use: Is the system user-friendly and easy to learn?
- Scalability: Can the system grow with your business?
- Integrations: Does the system integrate with your existing tools and systems, such as your website, email marketing platform, and accounting software?
- Pricing: What is the pricing structure? Does it fit within your budget?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer adequate customer support?
- Reviews and Reputation: What are other users saying about the system?
Some popular CRM systems for small retail businesses include:
- Zoho CRM: A comprehensive CRM with a wide range of features, suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- HubSpot CRM: A free, user-friendly CRM with excellent marketing automation capabilities.
- Salesforce Essentials: A simplified version of Salesforce, designed for small businesses.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM designed to streamline the sales process.
- Freshsales: A user-friendly CRM with a focus on sales and customer support.
3. Evaluate and Compare Systems
Once you’ve researched several CRM systems, it’s time to evaluate and compare them. Create a spreadsheet or document to compare the features, pricing, and other factors that are important to you. Consider:
- Free Trials or Demos: Take advantage of free trials or demos to test out the system and see if it meets your needs.
- User Reviews: Read user reviews and testimonials to get a better understanding of the system’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Pricing Plans: Compare the different pricing plans and choose the one that best fits your budget and needs.
- Integration Capabilities: Assess the system’s ability to integrate with your existing tools and systems.
4. Choose the Right System
Based on your evaluation, choose the CRM system that best meets your needs and goals. Consider the long-term implications of your decision and choose a system that can grow with your business.
Implementing Your CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide for Small Retailers
Once you’ve chosen your CRM system, the real work begins: implementation. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you successfully implement your CRM and maximize its benefits:
1. Plan Your Implementation
Before you start implementing your CRM, create a detailed implementation plan. This plan should include:
- Project Timeline: Set realistic timelines for each stage of the implementation process.
- Resources: Identify the resources you’ll need, such as staff time, training materials, and technical support.
- Data Migration Plan: Plan how you’ll migrate your existing customer data into the new CRM system.
- Training Plan: Develop a training plan to ensure your team is comfortable using the new system.
- Communication Plan: Communicate the implementation plan to your team and keep them informed of the progress.
2. Data Migration
Migrating your existing customer data into the new CRM system is a critical step. Ensure your data is accurate, clean, and organized before importing it. Consider the following:
- Data Cleanup: Remove duplicate entries, correct errors, and standardize your data format.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in the new CRM system.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM system, following the vendor’s instructions.
- Data Verification: Verify that your data has been imported correctly and that all fields are populated as expected.
3. System Configuration
Configure the CRM system to meet your specific needs. This may include:
- Customizing Fields: Add custom fields to capture specific information relevant to your business.
- Setting Up Workflows: Create automated workflows to streamline your processes.
- Integrating with Other Systems: Integrate the CRM with your other tools and systems.
- Setting Up User Permissions: Configure user permissions to control access to different features and data.
4. Training and Onboarding
Provide comprehensive training to your team to ensure they are comfortable using the new CRM system. Training should cover:
- Basic Navigation: Teach users how to navigate the system and access different features.
- Data Entry: Train users on how to enter and update customer data.
- Workflow Automation: Explain how to use automated workflows to streamline tasks.
- Reporting and Analytics: Show users how to generate reports and analyze data.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support and resources to help users adopt the new system.
5. Testing and Refinement
Before fully launching the CRM system, test it thoroughly to ensure it’s working correctly. Identify and address any issues before they impact your business. Refine your processes based on user feedback and your own experience.
6. Ongoing Management and Optimization
CRM implementation is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor your CRM usage, gather feedback from your team, and optimize your processes to maximize its benefits. This includes:
- Regular Data Updates: Keep your customer data up-to-date and accurate.
- Process Optimization: Continuously refine your workflows and processes.
- User Training: Provide ongoing training to keep your team up-to-date on the latest features and best practices.
- Performance Monitoring: Track key metrics and identify areas for improvement.
- Seek Support: Stay in touch with your CRM vendor for updates and support.
Best Practices for CRM Success in Small Retail
To ensure the success of your CRM implementation, follow these best practices:
- Start Small: Don’t try to implement everything at once. Start with a few key features and gradually expand your use of the system.
- Get Buy-In: Involve your team in the implementation process and get their buy-in.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensure your data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date.
- Use Automation Wisely: Automate tasks where it makes sense, but don’t overdo it.
- Personalize Your Interactions: Use the CRM to personalize your interactions with customers.
- Measure Your Results: Track key metrics to measure the success of your CRM implementation.
- Seek Expert Advice: If needed, consider seeking expert advice from a CRM consultant.
- Stay Flexible: Be prepared to adapt your strategies and processes as your business evolves.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a CRM system can present some challenges. Here’s how to overcome them:
- Lack of User Adoption: Ensure your team is properly trained and that the system is easy to use. Address any concerns and provide ongoing support.
- Data Quality Issues: Implement data cleaning and validation procedures to ensure your data is accurate.
- Integration Problems: Carefully plan your integrations and test them thoroughly.
- Cost Concerns: Choose a CRM system that fits your budget and offers a good return on investment.
- Time Constraints: Allocate sufficient time and resources to the implementation process.
The Future of CRM in Retail
The retail landscape is constantly evolving, and CRM technology is keeping pace. Here are some trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered CRM systems can automate tasks, personalize customer experiences, and provide valuable insights.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM apps allow retailers to access customer data and manage interactions on the go.
- Omnichannel CRM: Omnichannel CRM systems integrate data from all customer touchpoints, providing a unified view of the customer journey.
- Personalization: Retailers are increasingly using CRM to personalize their marketing, sales, and customer service efforts.
- Data Privacy: Data privacy is becoming increasingly important, and CRM systems are adapting to meet these evolving requirements.
By embracing these trends, small retail businesses can stay ahead of the curve and continue to build strong customer relationships.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Retail Success
In today’s competitive retail environment, a CRM system is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. By implementing a CRM, small retail businesses can:
- Enhance Customer Relationships: Build stronger, more loyal customer relationships.
- Increase Sales and Marketing Effectiveness: Improve your sales and marketing results.
- Streamline Operations: Improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Make Data-Driven Decisions: Make informed decisions based on data insights.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can successfully implement a CRM system and unlock the full potential of your small retail business. Take the first step today and start building a customer-centric business that thrives.