Boost Your Small Retail Business: The Ultimate Guide to CRM
Boost Your Small Retail Business: The Ultimate Guide to CRM
Running a small retail business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling inventory, managing staff, keeping up with the latest trends, and, oh yeah, trying to make a profit. In the midst of all this, it’s easy for customer relationships to fall by the wayside. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system steps in – a game-changer for small retail businesses looking to thrive.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of CRM, specifically tailored for small retail businesses. We’ll explore what CRM is, why it’s essential, the key features to look for, how to choose the right system, and how to implement it successfully. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how CRM can transform your business, fostering stronger customer connections, driving sales, and ultimately, helping you achieve lasting success.
What is CRM and Why Does Your Small Retail Business Need It?
Let’s start with the basics. CRM, at its core, is a strategy and a technology for managing all your company’s relationships and interactions with current and potential customers. Think of it as a central hub for all customer-related information. It’s not just about storing data; it’s about using that data to understand your customers better and provide them with exceptional experiences.
For a small retail business, this translates into:
- Improved Customer Service: Quickly accessing customer information allows your staff to provide personalized service, resolve issues efficiently, and build rapport.
- Increased Sales: Understanding customer preferences and purchase history enables you to offer targeted promotions, recommend relevant products, and ultimately, increase sales.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: Personalized interactions and proactive communication foster a sense of value and encourage repeat business.
- Streamlined Operations: CRM automates many repetitive tasks, freeing up your time to focus on more strategic initiatives like growing your business.
- Better Decision-Making: Data-driven insights from CRM help you understand customer behavior, track sales trends, and make informed decisions about your inventory, marketing, and overall business strategy.
In essence, CRM isn’t just a luxury; it’s a necessity for small retail businesses that want to compete in today’s dynamic market. It’s about creating a customer-centric approach that puts your customers at the heart of everything you do.
Key Features of a CRM System for Small Retail Businesses
Not all CRM systems are created equal. When choosing a CRM for your small retail business, focus on features that align with your specific needs and goals. Here are some essential features to consider:
Contact Management
This is the foundation of any good CRM. Contact management allows you to store and organize customer information, including:
- Contact Details: Names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles.
- Purchase History: A record of what customers have bought, when they bought it, and how much they spent.
- Communication History: Records of all interactions with customers, including emails, phone calls, and in-person conversations.
- Customer Segmentation: The ability to group customers based on demographics, purchase behavior, or other criteria.
Effective contact management ensures you have a complete view of each customer, enabling you to personalize your interactions and tailor your marketing efforts.
Sales Automation
Sales automation streamlines your sales processes, saving you time and effort. Key features include:
- Lead Management: Tracking and nurturing leads from initial contact to conversion.
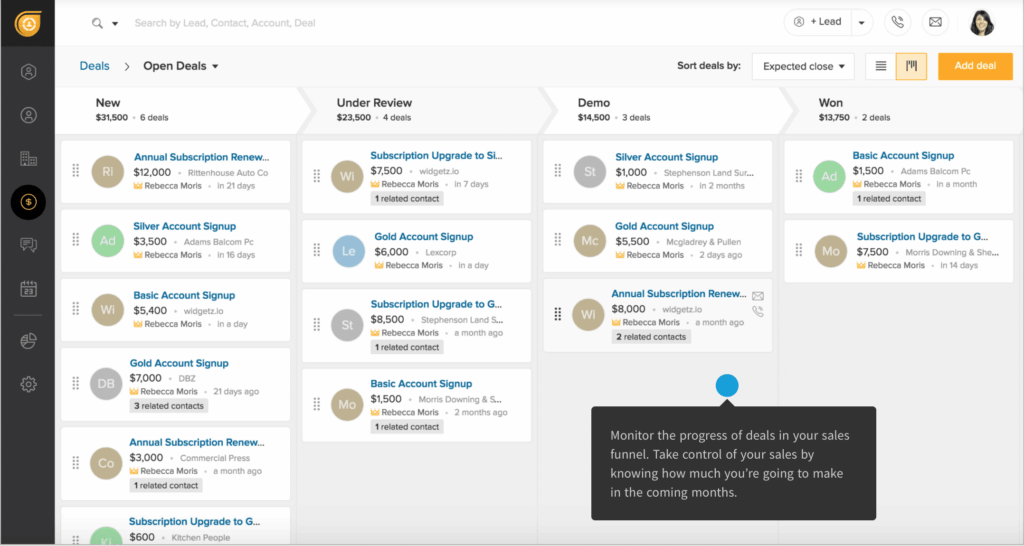
- Sales Pipeline Management: Visualizing your sales process and tracking the progress of deals.
- Automated Email Marketing: Sending targeted email campaigns based on customer behavior or preferences.
- Task Automation: Automating repetitive tasks like sending follow-up emails or scheduling appointments.
By automating these tasks, you can free up your time to focus on closing deals and building relationships.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation helps you create and manage targeted marketing campaigns. Key features include:
- Email Marketing: Creating and sending email newsletters, promotional offers, and other marketing communications.
- Social Media Integration: Connecting your CRM with your social media accounts to track customer interactions and manage your social media presence.
- Campaign Management: Planning, executing, and tracking the results of your marketing campaigns.
- Personalization: Customizing your marketing messages based on customer data and preferences.
Marketing automation allows you to reach the right customers with the right message at the right time, driving engagement and sales.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into your sales, marketing, and customer service performance. Key features include:
- Sales Reports: Tracking sales trends, revenue, and other key metrics.
- Customer Behavior Analysis: Understanding customer purchase patterns, preferences, and behavior.
- Marketing Campaign Performance: Measuring the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
- Customizable Dashboards: Creating dashboards that display the metrics most important to your business.
By analyzing your data, you can identify areas for improvement, optimize your strategies, and make data-driven decisions.
Inventory Management Integration (Optional but Highly Recommended)
Integrating your CRM with your inventory management system can provide a seamless view of your business operations. This allows you to:
- Track Inventory Levels: Monitor stock levels and receive alerts when items are running low.
- Manage Orders: Process orders efficiently and track their status.
- Predict Demand: Analyze sales data to forecast future demand and optimize your inventory.
This integration can save you time, reduce errors, and improve your overall efficiency.
Choosing the Right CRM System for Your Small Retail Business
Selecting the right CRM can feel overwhelming, but by following a structured approach, you can find the perfect fit for your business. Consider these steps:
1. Define Your Needs and Goals
Before you start shopping, take the time to define your specific needs and goals. Ask yourself:
- What are your biggest customer service challenges?
- What are your sales goals?
- What marketing activities do you want to automate?
- What data do you need to track and analyze?
The answers to these questions will help you identify the essential features you need in a CRM system.
2. Research CRM Vendors
Once you know your needs, research different CRM vendors. Look for vendors that specialize in small businesses or have a strong track record in the retail industry. Consider factors like:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need?
- Ease of Use: Is the system user-friendly and easy to learn?
- Pricing: Is the pricing affordable and scalable?
- Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with your existing systems, such as your point-of-sale (POS) system, email marketing platform, and accounting software?
- Customer Support: Does the vendor offer good customer support?
- Reviews and Testimonials: What do other users say about the CRM?
3. Consider Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise CRM
There are two main types of CRM systems: cloud-based and on-premise.
- Cloud-Based CRM: Hosted on the vendor’s servers, accessible via the internet. Cloud-based CRMs are generally more affordable, easier to set up, and require less technical expertise.
- On-Premise CRM: Installed on your own servers. On-premise CRMs offer more control over your data but require more technical expertise and can be more expensive to set up and maintain.
For most small retail businesses, a cloud-based CRM is the best option.
4. Get Free Trials and Demos
Many CRM vendors offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test the system and see if it’s a good fit for your business. Try out the key features and see how easy it is to use.
5. Choose the Right Plan
CRM vendors typically offer different pricing plans based on the features and the number of users. Choose the plan that best meets your needs and budget. Be sure to factor in the cost of training and any additional services you may need.
Implementing Your CRM System: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve chosen your CRM, it’s time to implement it. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Plan Your Implementation
Before you start, create a detailed implementation plan. This plan should include:
- Timeline: Set realistic deadlines for each stage of the implementation process.
- Team: Identify the people who will be involved in the implementation, including your internal team and any external consultants.
- Data Migration: Plan how you will migrate your existing data into the CRM system.
- Training: Schedule training for your staff on how to use the CRM system.
- Testing: Test the system thoroughly before you go live.
2. Data Migration
Migrating your data from your existing systems into your CRM is a crucial step. Ensure your data is clean, accurate, and organized. Consider these points:
- Data Import Tools: Most CRM systems offer data import tools that allow you to upload your data from spreadsheets or other databases.
- Data Cleaning: Clean up your data before you import it. Remove duplicates, correct errors, and standardize your data format.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in your CRM system.
3. Customize Your CRM
Customize your CRM to meet your specific needs. This may involve:
- Adding Custom Fields: Add custom fields to store information that is unique to your business.
- Configuring Workflows: Set up workflows to automate tasks and streamline your processes.
- Integrating with Other Systems: Integrate your CRM with your other systems, such as your POS system and email marketing platform.
4. Train Your Staff
Training your staff is essential for the success of your CRM implementation. Provide comprehensive training on how to use the system, including:
- Basic Navigation: Show your staff how to navigate the system and find the information they need.
- Data Entry: Train your staff on how to enter and update customer data.
- Using Key Features: Train your staff on how to use the key features of the CRM, such as contact management, sales automation, and marketing automation.
- Best Practices: Provide your staff with best practices for using the CRM to build strong customer relationships.
5. Go Live and Monitor Your Progress
Once you’ve completed the above steps, it’s time to go live. Start using the CRM system and monitor your progress. Track key metrics, such as:
- Customer Satisfaction: Measure customer satisfaction through surveys or feedback forms.
- Sales Growth: Track your sales and revenue to see if your CRM is driving sales.
- Customer Retention: Monitor your customer retention rate to see if your CRM is helping you retain customers.
- User Adoption: Track how frequently your staff is using the CRM.
Make adjustments as needed to optimize your CRM system and achieve your goals.
Tips for CRM Success in Your Small Retail Business
Implementing a CRM is a journey, not a destination. Here are some tips to help you achieve CRM success:
- Start Small: Don’t try to implement everything at once. Start with the essential features and gradually add more features as you become more comfortable with the system.
- Get Buy-In from Your Team: Involve your team in the implementation process and get their input. This will help them feel invested in the system and more likely to use it.
- Provide Ongoing Training and Support: Offer ongoing training and support to your staff to help them stay up-to-date on the latest features and best practices.
- Regularly Review and Optimize: Regularly review your CRM system and make adjustments as needed to optimize its performance and achieve your goals.
- Focus on Data Quality: Ensure your data is accurate and up-to-date. This is essential for making data-driven decisions.
- Prioritize Customer Experience: Always put your customers first. Use your CRM to provide personalized service and build strong relationships.
- Integrate with Your POS System: If possible, integrate your CRM with your POS system to get a complete view of your customer interactions.
- Automate, Automate, Automate: Leverage automation features to streamline your processes and free up your time.
The Benefits of CRM for Small Retail: A Recap
Let’s revisit the key benefits of implementing a CRM system in your small retail business:
- Improved Customer Relationships: CRM helps you understand your customers better and build stronger relationships.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: CRM enables you to target your marketing efforts and increase sales.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: CRM helps you retain customers and build brand loyalty.
- Streamlined Operations: CRM automates tasks and streamlines your processes.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: CRM provides valuable insights into your business performance.
- Competitive Advantage: CRM helps you stay ahead of the competition by providing exceptional customer service.
Investing in a CRM system is an investment in your future. It’s a powerful tool that can transform your business and help you achieve lasting success.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While CRM offers numerous benefits, there can be challenges during implementation and usage. Here’s how to address some common hurdles:
1. Resistance to Change
Some employees may resist adopting a new system. To overcome this:
- Communicate the benefits: Clearly explain how CRM will improve their work and the overall customer experience.
- Involve them in the process: Seek their input during the selection and implementation phases.
- Provide adequate training and support: Ensure they feel comfortable using the system.
- Lead by example: Demonstrate the value of CRM through your own actions.
2. Data Migration Difficulties
Migrating data can be complex. Address this by:
- Planning thoroughly: Create a detailed data migration plan.
- Cleaning your data: Remove duplicates and correct errors before importing.
- Using import tools effectively: Leverage the CRM’s data import capabilities.
- Seeking expert help: Consider hiring a consultant if you’re struggling with data migration.
3. Lack of User Adoption
If employees don’t use the CRM, its benefits are lost. Improve adoption by:
- Making it user-friendly: Choose a CRM that’s easy to navigate and use.
- Providing ongoing training: Offer regular training sessions and refresher courses.
- Highlighting success stories: Share examples of how the CRM has improved customer interactions.
- Monitoring usage and providing feedback: Track user activity and offer support to those who need it.
4. Integration Challenges
Integrating with other systems can be tricky. Mitigate this by:
- Choosing a CRM with good integration capabilities: Ensure the CRM integrates with your key systems.
- Planning your integrations carefully: Map out the data flow between systems.
- Testing thoroughly: Verify that integrations are working correctly before going live.
- Seeking technical support: Don’t hesitate to contact the CRM vendor or a consultant if you encounter issues.
5. Maintaining Data Quality
Poor data quality undermines the effectiveness of your CRM. Improve data quality by:
- Establishing data entry standards: Define clear guidelines for entering data.
- Providing data entry training: Ensure employees understand how to enter data accurately.
- Implementing data validation rules: Use the CRM’s features to validate data entry.
- Regularly reviewing and cleaning your data: Schedule periodic data cleansing activities.
The Future of CRM in Retail: Trends to Watch
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving. Here are some trends that are shaping the future of CRM in retail:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered CRM systems are becoming increasingly common, offering features like predictive analytics, chatbots, and personalized recommendations.
- Mobile CRM: Mobile CRM apps allow you to access and manage your customer data on the go, providing greater flexibility and convenience.
- Omnichannel CRM: Omnichannel CRM systems integrate data from all your customer touchpoints, providing a unified view of your customer interactions.
- Social CRM: Social CRM integrates your CRM with your social media accounts, allowing you to track customer interactions and manage your social media presence.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs are emerging as a way to centralize and manage customer data from multiple sources, providing a 360-degree view of your customers.
By staying informed about these trends, you can ensure that your CRM system remains effective and helps you stay ahead of the competition.
Conclusion: Embracing CRM for Retail Success
In the competitive world of small retail, CRM is no longer optional; it’s a strategic imperative. By implementing a well-chosen and effectively utilized CRM system, you can transform your business, build stronger customer relationships, drive sales, and achieve lasting success.
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of CRM for small retail businesses. From understanding the core features to navigating the implementation process, you now have the knowledge and tools you need to make informed decisions and take your business to the next level. Embrace the power of CRM, and watch your small retail business flourish.





