The Ultimate Small Business CRM Implementation Guide: From Zero to Success
Introduction: Why Your Small Business Needs a CRM
So, you’re running a small business. Congratulations! That’s a huge accomplishment. You’re juggling a million things – from product development and marketing to customer service and accounting. It’s a wild ride, isn’t it? And in the middle of all that chaos, you’ve likely realized something: keeping track of everything is… well, a monumental task. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. Think of it as your business’s central nervous system, connecting all the dots and streamlining your operations.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of implementing a CRM for your small business. We’ll cover everything from understanding the benefits and choosing the right software to the nitty-gritty details of data migration, user training, and ongoing optimization. Forget the jargon and the complicated tech speak. We’re going to break it all down into easy-to-understand steps. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and confidence to successfully implement a CRM and transform your business.
What is a CRM and Why Does Your Small Business Need One?
Let’s start with the basics. CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. At its core, a CRM is a software solution designed to manage your interactions with current and potential customers. It’s more than just a contact database; it’s a powerful tool that can help you:
- Improve Customer Relationships: By centralizing customer data, you can personalize interactions and provide better service.
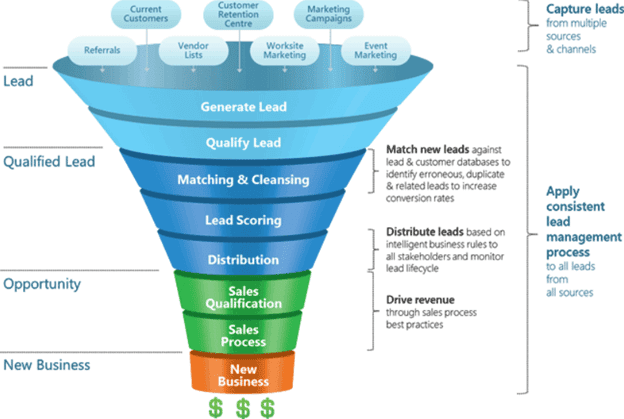
- Increase Sales: CRM helps you track leads, manage the sales pipeline, and close deals more efficiently.
- Boost Productivity: Automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Gain Valuable Insights: CRM provides data-driven insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness.
- Enhance Collaboration: Ensure everyone on your team has access to the same customer information, fostering better communication and teamwork.
For a small business, these benefits are crucial. You’re likely operating with limited resources, and every dollar and every minute counts. A CRM can help you maximize your efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately, grow your business. Without a CRM, you might be relying on spreadsheets, sticky notes, and scattered emails – a recipe for missed opportunities and frustrated customers. A CRM brings order to the chaos, allowing you to stay organized, informed, and in control.
Step 1: Assessing Your Needs and Defining Your Goals
Before you jump into selecting a CRM, take a step back and assess your current situation. What are your pain points? What are you hoping to achieve with a CRM? Defining your needs and goals is the foundation for a successful implementation. This step prevents you from getting overwhelmed by the vast array of features offered by different CRM systems and helps you choose the right one for your specific needs. Think of it like building a house – you wouldn’t start laying bricks without a blueprint, right?
Here’s a breakdown of what you need to do:
1.1. Identify Your Current Challenges
What are the biggest headaches in your current customer management process? Are you struggling with:
- Lost Leads? Are leads slipping through the cracks?
- Poor Communication? Are customers receiving inconsistent information?
- Inefficient Sales Processes? Are your salespeople spending too much time on administrative tasks?
- Lack of Visibility? Do you have a clear view of your sales pipeline and customer interactions?
- Data Silos? Is customer data scattered across different spreadsheets and systems?
Make a list of these challenges. This will help you prioritize the features you need in a CRM.
1.2. Define Your Goals
What do you want to achieve with a CRM? Be specific and set measurable goals. For example, instead of saying “improve customer satisfaction,” aim for “increase customer satisfaction scores by 15% within six months.” Other examples include:
- Increase Sales Revenue: Set a target percentage increase in sales.
- Reduce Sales Cycle Time: Aim to shorten the time it takes to close a deal.
- Improve Lead Conversion Rates: Set a target percentage increase in lead-to-customer conversion.
- Enhance Customer Retention: Set a target percentage increase in customer retention.
- Improve Customer Service Response Times: Set a target for reducing response times.
Having clear goals will help you measure the success of your CRM implementation.
1.3. Understand Your Budget
CRM systems come in various price ranges, from free to enterprise-level solutions. Determine how much you’re willing to spend on a CRM, taking into account the following costs:
- Software Licensing Fees: This is the recurring cost for using the CRM software.
- Implementation Costs: This includes the cost of data migration, customization, and training.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance: Factor in the cost of technical support and system maintenance.
- Hardware Costs: Consider any hardware requirements, such as servers or additional computers.
Having a clear budget will help you narrow down your CRM options.
1.4. Involve Your Team
Don’t make this decision in a vacuum. Involve your team members, especially those who will be using the CRM daily. Get their input on their needs and preferences. This will increase buy-in and make the implementation process smoother. Conduct surveys, hold brainstorming sessions, and gather feedback from your team.
Step 2: Choosing the Right CRM Software
Now for the fun part! Choosing the right CRM can feel overwhelming, but by following the steps above, you’ve already narrowed down your options. The key is to find a system that aligns with your needs, goals, and budget. There are tons of CRM solutions on the market, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. This section breaks down the key factors to consider when making your selection.
2.1. Research and Compare CRM Systems
Start by researching the top CRM systems for small businesses. Some popular options include:
- HubSpot CRM: A free, all-in-one CRM that’s great for small businesses just starting out. It offers a wide range of features, including contact management, sales pipeline tracking, and marketing automation.
- Zoho CRM: A feature-rich CRM that offers a wide range of customization options. It’s a good choice for businesses that need a lot of flexibility.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A powerful CRM that’s suitable for businesses of all sizes. It offers a comprehensive set of features, but it can be more complex to set up and manage.
- Pipedrive: A sales-focused CRM that’s designed to help sales teams close deals faster. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive sales pipeline management.
- Freshsales: A CRM that’s known for its ease of use and affordability. It’s a good choice for businesses that are looking for a simple and straightforward CRM solution.
Read reviews, compare features, and create a shortlist of potential candidates. Consider the following factors:
- Features: Does the CRM offer the features you need, such as contact management, sales pipeline management, marketing automation, and customer service tools?
- Ease of Use: Is the CRM user-friendly and easy to learn?
- Scalability: Can the CRM grow with your business?
- Integrations: Does the CRM integrate with the other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and social media channels?
- Pricing: Does the CRM fit within your budget?
- Customer Support: Does the CRM provider offer good customer support?
2.2. Consider Specific Industry Needs
Some CRM systems are designed for specific industries. If you’re in a niche industry, consider whether there are CRM solutions tailored to your needs. For example, real estate businesses might benefit from a CRM with features for managing property listings and client relationships, while a healthcare provider might need a CRM with features for patient management and appointment scheduling.
2.3. Take Advantage of Free Trials and Demos
Most CRM providers offer free trials or demos. Take advantage of these opportunities to test out the software and see if it’s a good fit for your business. During the trial, explore the features, experiment with different functionalities, and get a feel for the user interface. This will help you make a more informed decision.
2.4. Prioritize User Experience
A CRM is only as good as the people who use it. Choose a CRM that’s user-friendly and intuitive. If your team finds the CRM difficult to use, they won’t use it, and your implementation will fail. Look for a CRM with a clean interface, easy navigation, and helpful tutorials.
Step 3: Planning Your CRM Implementation
You’ve chosen your CRM, now it’s time to create a detailed implementation plan. This is where you map out the steps you need to take to get your CRM up and running. A well-defined plan will ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions to your business. This is where the rubber meets the road. Let’s dive in.
3.1. Define Your Implementation Scope
Determine the scope of your CRM implementation. Will you implement all features at once, or will you roll out the CRM in phases? A phased approach can be less overwhelming and allow you to learn and adapt as you go. Consider starting with core features, such as contact management and sales pipeline tracking, and then gradually adding more advanced functionalities.
3.2. Data Migration Strategy
Data migration is the process of transferring your existing customer data into your new CRM. This is a critical step, and it’s important to plan it carefully. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Data Cleaning: Before you migrate your data, clean it up. Remove duplicates, correct errors, and standardize data formats.
- Data Mapping: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in your new CRM.
- Data Import: Import your data into the CRM. Most CRM systems offer import tools to simplify this process.
- Data Validation: After importing your data, validate it to ensure that it’s accurate and complete.
Consider using a data migration tool to automate the process and minimize errors. If you have a large amount of data, you might consider hiring a data migration specialist.
3.3. Customize Your CRM
Most CRM systems offer customization options to tailor the software to your specific needs. Customize the CRM to match your sales process, workflows, and reporting requirements. This might involve:
- Creating Custom Fields: Add custom fields to capture specific information about your customers.
- Customizing Workflows: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending follow-up emails and updating deal stages.
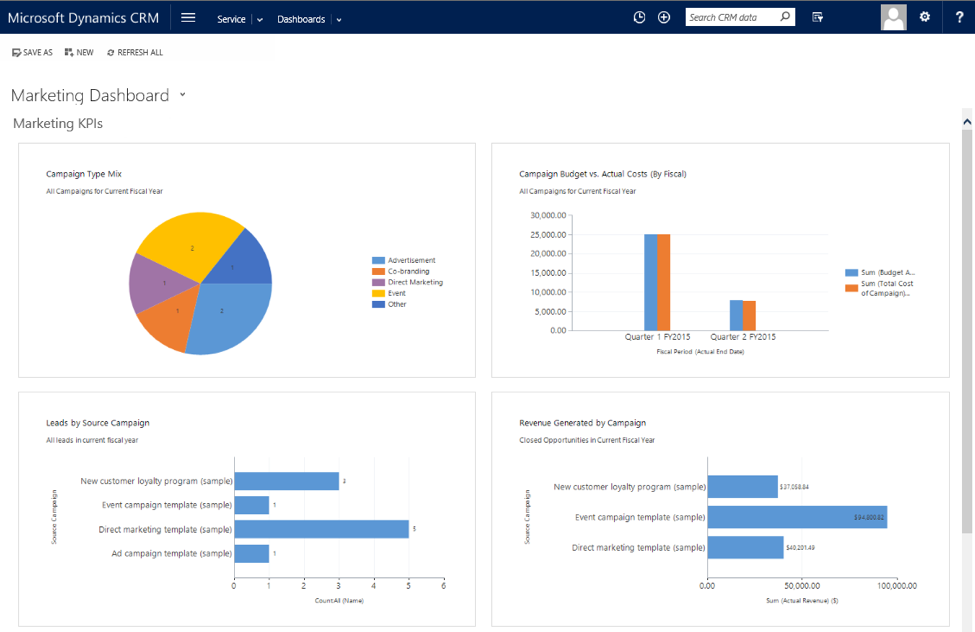
- Setting Up Reports and Dashboards: Create reports and dashboards to track key metrics and gain insights into your business performance.
- Configuring User Roles and Permissions: Assign different roles and permissions to users to control access to data and features.
Take the time to configure your CRM to your specifications. This will make it more useful and effective for your team.
3.4. Integrate with Other Tools
Integrate your CRM with other tools you use, such as your email marketing platform, accounting software, and social media channels. This will streamline your workflows and eliminate the need to manually transfer data between systems. Integrations will save you time and reduce the potential for errors.
Step 4: Implementing Your CRM
Now, it’s time to execute your plan. This is where you put everything into action. With a well-defined plan, the implementation phase should be relatively smooth. However, be prepared for unexpected challenges and be flexible enough to adapt as needed. Let’s make it happen!
4.1. Data Import and Validation
Carefully import your data into the CRM, following the data migration strategy you defined. After importing the data, validate it to ensure its accuracy. Check for any missing data, errors, or inconsistencies. If you find any issues, correct them and re-import the data. This is a critical step to ensure the accuracy of your CRM data.
4.2. User Training
Train your team on how to use the CRM. Provide comprehensive training on all relevant features and functionalities. Offer different training methods, such as:
- Instructor-led training: In-person or virtual training sessions led by a CRM expert.
- Online tutorials and documentation: Provide access to online tutorials, user manuals, and FAQs.
- Hands-on practice: Encourage users to practice using the CRM in a test environment.
Make sure everyone understands how to use the CRM effectively. This is crucial for maximizing adoption and ensuring the success of your implementation.
4.3. Test and Refine
Before going live, test the CRM thoroughly. Make sure everything is working as expected. Test different scenarios, such as creating new contacts, updating deal stages, and generating reports. Gather feedback from your team and make any necessary adjustments. This is the time to iron out any wrinkles and ensure a smooth launch.
4.4. Go Live!
Once you’re confident that everything is working correctly, it’s time to go live. Announce the launch to your team and provide ongoing support. Be prepared to answer questions and address any issues that arise. Celebrate the launch and acknowledge the hard work of your team.
Step 5: User Adoption and Training
Successfully implementing a CRM is only half the battle. The real challenge lies in ensuring that your team actually *uses* the CRM. This is where user adoption and ongoing training come into play. A CRM is only effective if your team embraces it and uses it consistently. Here’s how to foster user adoption and provide ongoing training.
5.1. Encourage User Adoption
Here are some strategies to encourage user adoption:
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly communicate the benefits of using the CRM to your team. Explain how it will make their jobs easier, improve their productivity, and help them achieve their goals.
- Lead by Example: Management should use the CRM actively and demonstrate its value.
- Provide Incentives: Offer incentives for users who consistently use the CRM and achieve their goals.
- Make it Easy to Use: Ensure the CRM is user-friendly and easy to navigate.
- Address Concerns: Listen to your team’s concerns and address any issues they may have.
- Foster a Culture of Collaboration: Encourage team members to share best practices and help each other use the CRM effectively.
5.2. Ongoing Training and Support
User training shouldn’t be a one-time event. Provide ongoing training and support to ensure that your team continues to use the CRM effectively. Offer:
- Refresher Training: Regular refresher training sessions to reinforce key concepts and features.
- New Feature Training: Training on new features as they are released.
- Help Desk and Support: Provide a help desk or support system to answer questions and resolve issues.
- User Documentation: Maintain up-to-date user documentation, such as user manuals, FAQs, and video tutorials.
- Regular Feedback: Encourage users to provide feedback and suggestions for improvement.
By providing ongoing training and support, you can ensure that your team continues to use the CRM effectively and get the most value from it.
Step 6: Measuring Success and Optimizing Your CRM
You’ve implemented your CRM, your team is using it, and things are starting to hum. But your work isn’t done! The final step is to measure the success of your CRM implementation and continuously optimize the system to improve its performance. This is a continuous process, not a one-time event. It’s about continually refining your CRM to meet your evolving business needs. Here’s how to do it.
6.1. Track Key Metrics
Remember those goals you set in Step 1? Now it’s time to measure your progress. Track key metrics to assess the effectiveness of your CRM. These metrics might include:
- Sales Revenue: Track your sales revenue to see if it has increased.
- Lead Conversion Rates: Monitor your lead conversion rates to see if they have improved.
- Sales Cycle Time: Measure the time it takes to close a deal to see if it has decreased.
- Customer Satisfaction: Track customer satisfaction scores to see if they have improved.
- Customer Retention Rates: Monitor your customer retention rates to see if they have increased.
- User Adoption Rates: Track how often your team is using the CRM.
Use the reports and dashboards in your CRM to track these metrics. Compare your results to your initial goals to see if you’re on track.
6.2. Analyze Data and Identify Areas for Improvement
Regularly analyze your CRM data to identify areas for improvement. Look for trends, patterns, and insights. For example, you might discover that a particular lead source is generating the most qualified leads or that a specific sales process is more effective than others. Use these insights to make data-driven decisions and optimize your CRM.
6.3. Refine Your Processes and Workflows
Based on your data analysis, refine your processes and workflows. For example, you might adjust your sales process to incorporate the most effective techniques or automate additional tasks to improve efficiency. Continuously refine your processes to maximize the value of your CRM.
6.4. Make Adjustments and Improvements
Make adjustments and improvements to your CRM based on your data analysis and feedback from your team. This might involve:
- Adding new features: Consider adding new features to meet evolving business needs.
- Customizing existing features: Customize existing features to improve their functionality.
- Updating user roles and permissions: Update user roles and permissions as needed.
- Providing additional training: Provide additional training to address any skill gaps.
Continuously monitor your CRM performance and make adjustments to ensure that it continues to meet your business needs.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Implementing a CRM can be a game-changer for your small business. However, there are some common pitfalls that can derail your implementation. Being aware of these potential issues can help you avoid them and ensure a successful outcome.
1.1. Not Defining Clear Goals
As we discussed earlier, defining clear goals is crucial. Without clear goals, it’s impossible to measure the success of your implementation. Make sure you have specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
1.2. Choosing the Wrong CRM
Choosing the wrong CRM can be a costly mistake. Take the time to research and compare different CRM systems to find the one that best fits your needs. Consider your budget, features, ease of use, and scalability.
1.3. Poor Data Migration
Poor data migration can result in data loss, errors, and inconsistencies. Take the time to clean and validate your data before migrating it into the CRM. Consider using a data migration tool or hiring a data migration specialist.
1.4. Lack of User Training
If your team doesn’t know how to use the CRM, it won’t be effective. Provide comprehensive training on all relevant features and functionalities. Offer different training methods, such as instructor-led training, online tutorials, and hands-on practice.
1.5. Neglecting Ongoing Support and Optimization
Implementing a CRM is not a one-time event. You need to provide ongoing support and continuously optimize the system to improve its performance. Track key metrics, analyze data, and refine your processes and workflows. Stay proactive and stay engaged.
Conclusion: CRM – Your Small Business Superpower
Implementing a CRM can be a transformative experience for your small business. By following this guide, you’ll be well on your way to selecting the right CRM, implementing it successfully, and maximizing its value. Remember, a CRM is more than just software; it’s a strategic tool that can help you improve customer relationships, increase sales, boost productivity, and gain valuable insights into your business. It’s a superpower that can help you navigate the challenges of running a small business and achieve sustainable growth.
The journey doesn’t end with implementation. It’s a continuous process of learning, adapting, and optimizing. Embrace the process, stay engaged, and never stop looking for ways to improve. With the right CRM and a commitment to continuous improvement, your small business can thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
So, take the first step. Assess your needs, choose the right CRM, and start your journey toward a more organized, efficient, and customer-centric business. The future is yours to build, and a CRM can be your most valuable ally.