Small Business CRM Implementation: Your Step-by-Step Guide to Customer Relationship Success

Introduction: Why a CRM is Your Small Business’s Secret Weapon
Running a small business is a whirlwind. You’re juggling everything from sales and marketing to customer service and operations. In the midst of all this, it’s easy for things to fall through the cracks, especially when it comes to managing customer relationships. That’s where a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system comes in. Think of it as your central hub for all things customer-related – a place to store information, track interactions, and ultimately, build stronger, more profitable relationships.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the entire process of implementing a CRM for your small business. We’ll cover everything from choosing the right CRM to training your team and optimizing your system for maximum impact. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for transforming your customer interactions and driving significant business growth.
Chapter 1: Understanding the Value of a CRM for Small Businesses
Before diving into the ‘how,’ let’s explore the ‘why.’ Why is a CRM so crucial for small businesses? The benefits are numerous and can be the difference between merely surviving and thriving in today’s competitive market. Here are some key advantages:
- Improved Customer Relationships: At its core, a CRM helps you understand your customers better. By centralizing customer data, you gain valuable insights into their preferences, purchase history, and communication patterns. This allows you to personalize your interactions, provide exceptional service, and foster long-term loyalty.
- Increased Sales: A CRM streamlines your sales process. It helps you track leads, manage opportunities, and automate follow-ups, ensuring that no potential customer slips through the cracks. This leads to more efficient sales cycles and a higher conversion rate.
- Enhanced Marketing Effectiveness: CRM systems enable targeted marketing campaigns. You can segment your customer base based on various criteria and tailor your messaging to specific groups. This results in higher engagement rates and a better return on investment (ROI) for your marketing efforts.
- Greater Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks, a CRM frees up your team’s time and allows them to focus on more strategic activities. This includes tasks like data entry, appointment scheduling, and email marketing.
- Improved Data Management: A CRM provides a centralized location for all customer data, eliminating the need for spreadsheets and scattered information. This ensures data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility.
- Better Decision-Making: With a CRM, you have access to real-time data and analytics, allowing you to make informed decisions about your business. You can track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and measure the effectiveness of your strategies.
In essence, a CRM empowers you to work smarter, not harder, and to build a customer-centric business that is poised for sustainable growth. It’s not just a software; it’s a strategic investment in your future.
Chapter 2: Choosing the Right CRM for Your Small Business
Selecting the right CRM is a critical decision. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, and the best choice for your business will depend on your specific needs, budget, and technical capabilities. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help you make the right choice:
Step 1: Define Your Needs and Objectives
Before you start comparing CRM options, take the time to clearly define your needs. What are your primary goals for implementing a CRM? What specific challenges are you hoping to solve? Consider these questions:
- What are your most pressing customer relationship challenges? Are you struggling with lead management, sales tracking, customer service, or something else?
- What features are essential for your business? Do you need sales automation, marketing automation, customer support ticketing, or integration with other tools?
- What is your budget? CRM pricing varies widely, so set a realistic budget upfront.
- How many users will need access to the CRM? This will affect the pricing and the level of support you require.
- What is your technical expertise? Some CRM systems are more complex than others. Consider your team’s technical skills and choose a system that they can easily learn and use.
Document your requirements and objectives. This will serve as your guide throughout the selection process.
Step 2: Research CRM Options
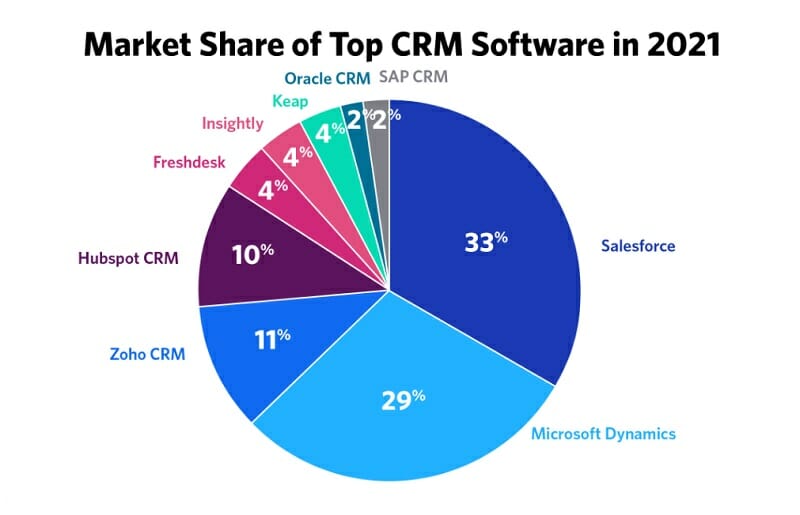
Once you’ve defined your needs, it’s time to research different CRM options. There are countless providers in the market, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are some popular options for small businesses:
- HubSpot CRM: A popular choice for its user-friendliness, free plan, and comprehensive features. It’s particularly well-suited for businesses that prioritize inbound marketing.
- Zoho CRM: Offers a wide range of features at a competitive price point. It’s a good option for businesses that need a robust and customizable CRM.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud: A powerful and feature-rich CRM that is suitable for businesses of all sizes. It offers a high degree of customization, but it can be more complex to set up and use.
- Freshsales: Designed with a focus on sales teams, offering features like lead scoring, sales automation, and phone integration.
- Pipedrive: Known for its visual sales pipeline and ease of use. It’s a great option for businesses that want a simple and intuitive CRM.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A comprehensive CRM that integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products. It’s a good choice for businesses that already use the Microsoft ecosystem.
Read reviews, compare features, and consider the pricing plans of each option. Look for CRM systems that offer a free trial so you can test them out before making a commitment.
Step 3: Prioritize Features
Not all CRM features are created equal. Once you have a shortlist of potential options, prioritize the features that are most important to your business. Consider the following:
- Contact Management: The ability to store and manage contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Lead Management: Tools for tracking leads, qualifying them, and assigning them to sales representatives.
- Sales Automation: Features for automating repetitive sales tasks, such as email follow-ups and appointment scheduling.
- Marketing Automation: Capabilities for creating and managing marketing campaigns, such as email marketing and social media integration.
- Customer Service: Tools for managing customer inquiries, resolving issues, and providing support.
- Reporting and Analytics: The ability to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate reports on sales, marketing, and customer service activities.
- Integration: The ability to integrate with other tools and applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
- Mobile Accessibility: The ability to access the CRM from mobile devices.
Create a feature matrix to compare the different CRM options and identify the one that best meets your needs.
Step 4: Consider Scalability and Support
Choose a CRM that can scale with your business. As your business grows, you’ll need a CRM that can handle an increasing number of users, contacts, and data. Also, consider the level of support offered by the CRM provider. Do they offer training, documentation, and customer support? Make sure the provider offers the kind of support you need.
Step 5: Try Before You Buy
Take advantage of free trials or demos to test out the CRM before making a decision. This will give you a hands-on experience and allow you to see how the CRM works in practice. Involve your team in the testing process to get their feedback and ensure that the CRM meets their needs.
By following these steps, you can choose the right CRM for your small business and set yourself up for success.
Chapter 3: Preparing for CRM Implementation
Before you launch your new CRM, careful preparation is essential. This involves data migration, team training, and process alignment. Taking the time to plan ahead will ensure a smooth implementation and maximize your chances of success.
Step 1: Data Migration
Data migration is the process of transferring your existing customer data from your old system (e.g., spreadsheets, contact lists, or other CRM systems) into your new CRM. This can be a complex task, but it’s crucial for ensuring that your CRM is populated with accurate and up-to-date information. Here’s how to approach data migration:
- Clean Your Data: Before migrating your data, take the time to clean it up. This involves removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing your data format.
- Map Your Data Fields: Map your existing data fields to the corresponding fields in your new CRM. This ensures that your data is transferred correctly.
- Choose a Migration Method: You can either manually enter your data into the CRM or use a data migration tool. If you have a large amount of data, a migration tool is recommended. Many CRM providers offer data migration services.
- Test Your Data: After migrating your data, test it to ensure that it has been transferred correctly. Check for any errors or inconsistencies.
- Back Up Your Data: Always back up your data before starting the migration process. This will protect your data in case of any problems.
Data migration can be time-consuming, but it’s worth the effort to ensure that your CRM is populated with accurate and reliable information. Consider hiring a data migration specialist or working with your CRM provider to streamline the process.
Step 2: Team Training
Your team is the key to the success of your CRM implementation. They need to be trained on how to use the CRM effectively. Here’s how to approach team training:
- Identify Training Needs: Determine the specific training needs of each team member. What features will they be using? What are their existing skills and knowledge?
- Develop a Training Plan: Create a training plan that outlines the training objectives, content, and schedule.
- Choose a Training Method: You can use a variety of training methods, such as online tutorials, in-person workshops, and on-the-job training.
- Provide Ongoing Training: Training shouldn’t be a one-time event. Provide ongoing training and support to help your team stay up-to-date on the latest features and best practices.
- Create User Guides and Documentation: Develop user guides and documentation to help your team use the CRM effectively.
Invest in comprehensive training to ensure that your team is comfortable and proficient with the new CRM system. This will lead to greater adoption and better results.
Step 3: Process Alignment
Your CRM implementation should align with your existing business processes. This involves identifying your key processes and mapping them to the CRM. Here’s how to approach process alignment:
- Document Your Processes: Document your existing customer-facing processes, such as lead management, sales, and customer service.
- Map Your Processes to the CRM: Determine how your processes will be implemented in the CRM.
- Identify Gaps and Opportunities for Improvement: Identify any gaps or opportunities for improvement in your processes.
- Optimize Your Processes: Optimize your processes to maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
- Document Your New Processes: Document your new processes and provide training to your team.
Process alignment is crucial for ensuring that your CRM is integrated seamlessly into your business operations. It will help you streamline your workflows, improve efficiency, and enhance the customer experience.
Chapter 4: Implementing Your CRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve chosen your CRM and prepared your team and data, it’s time to implement the system. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Step 1: Set Up Your CRM
The first step is to set up your CRM. This involves configuring the system to meet your specific needs. Here’s what you’ll need to do:
- Customize Your Settings: Customize your CRM settings, such as your company information, currency, and time zone.
- Add Users and Assign Roles: Add your team members to the CRM and assign them appropriate roles and permissions.
- Customize Your Fields and Layouts: Customize the fields and layouts to match your business needs. This includes adding custom fields, modifying existing fields, and arranging the layout of your screens.
- Configure Integrations: Configure integrations with other tools and applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
- Set Up Your Sales Pipeline: Set up your sales pipeline to track your sales opportunities.
Take your time to configure your CRM correctly. This will ensure that it works effectively for your business.
Step 2: Import Your Data
As discussed earlier, importing your data is a critical step. Follow the data migration steps outlined in Chapter 3 to import your customer data into the CRM.
Step 3: Train Your Team
Provide comprehensive training to your team on how to use the CRM. This includes training on the core features, best practices, and your specific business processes.
Step 4: Test the System
Before you go live, test the system thoroughly. This includes testing the functionality of the CRM, the accuracy of your data, and the performance of your integrations. Involve your team in the testing process to get their feedback.
Step 5: Go Live
Once you’ve completed the testing phase, it’s time to go live. Announce the launch to your team and provide ongoing support. Monitor the system closely and address any issues that arise.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize
After you go live, monitor the system closely and track your progress. Analyze your data to identify areas for improvement. Optimize your CRM settings, processes, and training to maximize your results.
Chapter 5: Optimizing Your CRM for Maximum Impact
Implementing a CRM is just the first step. To truly maximize its impact, you need to continuously optimize your system. Here’s how:
Step 1: Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify the KPIs that are most important to your business. These might include sales revenue, conversion rates, customer satisfaction scores, and customer lifetime value. Track these KPIs regularly to measure your progress and identify areas for improvement.
Step 2: Analyze Your Data
Use your CRM data to gain insights into your customers, sales processes, and marketing campaigns. Identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Use this data to make informed decisions about your business.
Step 3: Customize Your CRM
Regularly review your CRM settings and customize them to meet your evolving needs. This includes adding custom fields, modifying existing fields, and adjusting your workflows. As your business changes, your CRM should adapt with it.
Step 4: Automate Tasks
Use automation features to streamline your workflows and free up your team’s time. This includes automating tasks such as email follow-ups, appointment scheduling, and data entry.
Step 5: Integrate with Other Tools
Integrate your CRM with other tools and applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms. This will help you streamline your workflows and improve data accuracy.
Step 6: Regularly Review and Update Your Processes
Regularly review your business processes and update them as needed. This includes identifying any bottlenecks, optimizing your workflows, and improving your team’s efficiency.
Step 7: Seek User Feedback
Gather feedback from your team and customers to identify areas for improvement. This will help you understand how your CRM is being used and what improvements can be made.
Step 8: Provide Ongoing Training and Support
Provide ongoing training and support to your team to ensure that they are comfortable and proficient with the CRM. This includes providing access to training materials, documentation, and support resources.
Chapter 6: Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a CRM, while incredibly beneficial, can come with its share of challenges. Being aware of these potential roadblocks can help you proactively address them and ensure a smoother implementation process. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them:
- Lack of User Adoption: One of the biggest challenges is getting your team to actually use the CRM. If employees don’t see the value, they may resist using it. Solution: Provide comprehensive training, highlight the benefits of using the CRM, and involve your team in the implementation process. Make the CRM easy to use and integrate it into their daily workflows.
- Poor Data Quality: If your data isn’t accurate and up-to-date, your CRM will be ineffective. Solution: Clean your data before importing it into the CRM. Implement data validation rules to ensure that new data is accurate. Regularly review and update your data.
- Resistance to Change: Some team members may resist the new CRM system. Solution: Communicate the benefits of the CRM clearly. Involve your team in the decision-making process. Provide ongoing support and training. Address any concerns promptly.
- Integration Issues: Integrating your CRM with other systems can be challenging. Solution: Choose a CRM that integrates well with your existing tools. Work with your CRM provider to troubleshoot any integration issues.
- Data Migration Difficulties: Migrating data from your old system to the new CRM can be a complex and time-consuming process. Solution: Plan your data migration carefully. Clean your data before migrating it. Use a data migration tool or work with a data migration specialist.
- Lack of Clear Objectives: Without clear objectives, it will be difficult to measure the success of your CRM implementation. Solution: Define your goals and objectives before implementing the CRM. Track your progress against these goals.
- Over-Customization: Customizing your CRM too much can make it difficult to maintain and update. Solution: Start with the core features and customize your CRM gradually. Avoid over-customization.
By anticipating these challenges and taking proactive steps to address them, you can increase your chances of a successful CRM implementation.
Chapter 7: Measuring the ROI of Your CRM
Determining the return on investment (ROI) of your CRM is crucial for justifying the investment and demonstrating its value to your business. Here’s how to measure your CRM’s ROI:
Step 1: Define Your Metrics
Identify the key metrics that you want to track. These metrics should be aligned with your business objectives. Common metrics include:
- Sales Revenue: Track your sales revenue before and after implementing the CRM.
- Conversion Rates: Measure your conversion rates at various stages of the sales pipeline.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the cost of acquiring new customers.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Estimate the total revenue you can expect from a customer over their relationship with your business.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measure customer satisfaction levels.
- Customer Retention Rate: Track the percentage of customers who stay with your business over a period of time.
- Sales Cycle Length: Measure the time it takes to close a deal.
- Marketing ROI: Measure the return on investment for your marketing campaigns.
Step 2: Establish a Baseline
Before you implement your CRM, establish a baseline for your key metrics. This will provide a benchmark for measuring your progress.
Step 3: Track Your Results
Track your key metrics regularly. Use your CRM’s reporting and analytics features to monitor your progress.
Step 4: Analyze Your Data
Analyze your data to identify any trends or patterns. Determine whether your CRM is having a positive impact on your key metrics.
Step 5: Calculate Your ROI
Calculate your ROI by comparing your results before and after implementing the CRM. Consider the cost of the CRM (including software, implementation, and training) and the benefits (such as increased sales revenue and improved customer satisfaction).
By measuring your ROI, you can demonstrate the value of your CRM and justify your investment. This will help you to secure continued investment in the CRM and ensure that it is being used effectively.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Customer Relationships
Implementing a CRM is a significant step for any small business looking to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. It’s an investment in your customers, your team, and your future. By following this comprehensive guide, you’ve gained the knowledge and tools necessary to choose, implement, and optimize a CRM system that will transform your customer relationships and drive sustainable growth.
Remember, a successful CRM implementation is not a one-time event. It’s an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, optimization, and adaptation. By staying focused on your customers, embracing the power of data, and empowering your team, you can harness the full potential of your CRM and build a thriving business that puts customer relationships at the heart of everything you do. The future of business is customer-centric, and with a well-implemented CRM, you’re well on your way to leading the charge.