Unlocking Growth: A Deep Dive into CRM Marketing Performance and How to Supercharge It
In today’s hyper-competitive business landscape, simply having a product or service isn’t enough. You need to connect with your audience, understand their needs, and build lasting relationships. That’s where CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and its impact on marketing performance come into play. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of CRM marketing, exploring its intricacies, benefits, and the strategies you can implement to achieve remarkable results. We’ll unravel the secrets to optimizing your CRM system, leveraging data, and ultimately, driving sustainable growth.
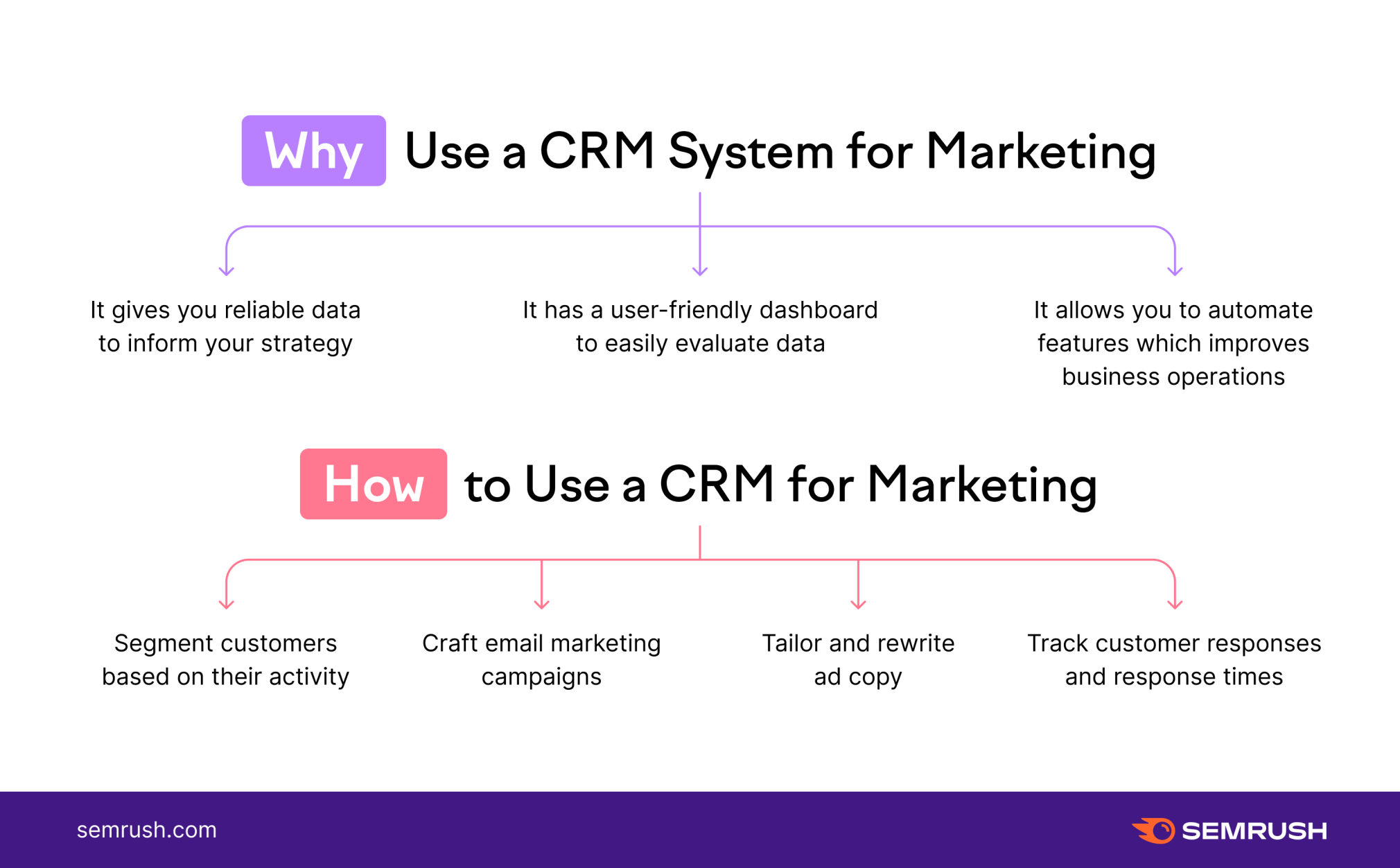
What is CRM and Why Does It Matter in Marketing?
At its core, CRM is a technology and strategy for managing all your company’s relationships and interactions with customers and potential customers. It’s not just about a software platform; it’s a philosophy centered on putting the customer first. In the context of marketing, CRM empowers you to:
- Understand Your Customers: Gather and analyze data about customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history.
- Personalize Your Marketing: Tailor your messaging and offers to individual customer needs and interests.
- Improve Customer Experience: Provide seamless and consistent interactions across all touchpoints.
- Increase Sales and Revenue: Identify and nurture leads, close deals more efficiently, and boost customer lifetime value.
- Optimize Marketing ROI: Track and measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
In essence, CRM transforms marketing from a guessing game into a data-driven science. It enables you to make informed decisions, target your efforts more effectively, and ultimately, achieve superior marketing performance.
Key Benefits of CRM for Marketing Performance
Implementing a well-executed CRM strategy can yield a plethora of benefits for your marketing efforts. Let’s explore some of the most significant:
Enhanced Customer Segmentation and Targeting
CRM allows you to segment your customer base based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchase history, website activity, and engagement with your marketing campaigns. This granular segmentation enables you to create highly targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups. For example, you can:
- Target high-value customers: Offer exclusive deals and personalized experiences to your most loyal customers.
- Re-engage inactive customers: Send targeted emails with special offers to win back lapsed customers.
- Nurture leads: Guide potential customers through the sales funnel with tailored content and offers.
By targeting the right customers with the right message at the right time, you can significantly improve your conversion rates and generate more qualified leads.
Improved Lead Management and Qualification
CRM systems streamline the lead management process, from capturing leads to qualifying them and passing them on to the sales team. This automation saves time and effort, ensuring that no leads fall through the cracks. Key benefits include:
- Lead Scoring: Assigning scores to leads based on their behavior and engagement, allowing you to prioritize the most promising leads.
- Automated Lead Nurturing: Sending automated email sequences to nurture leads and guide them through the sales funnel.
- Faster Response Times: Ensuring that leads receive timely follow-up and information.
By optimizing your lead management process, you can improve your conversion rates and reduce the time it takes to close deals.
Personalized Marketing Campaigns
CRM data empowers you to personalize your marketing campaigns, making them more relevant and engaging for your customers. Personalization goes beyond simply using a customer’s name in an email. It involves tailoring your messaging, offers, and content based on individual customer preferences, behavior, and purchase history. Examples of personalized marketing include:
- Personalized Product Recommendations: Suggesting products that are relevant to a customer’s past purchases or browsing history.
- Targeted Email Campaigns: Sending emails with content and offers that are tailored to a customer’s specific interests.
- Personalized Website Experiences: Customizing the content and offers that customers see when they visit your website.
Personalized marketing significantly increases customer engagement and conversion rates, leading to higher ROI.
Enhanced Customer Service and Support
CRM systems provide a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, including support tickets, inquiries, and feedback. This allows you to provide faster, more efficient, and more personalized customer service. Key benefits include:
- 360-Degree Customer View: Accessing a complete history of customer interactions, including purchase history, support tickets, and communication logs.
- Faster Resolution Times: Empowering your support team with the information they need to quickly resolve customer issues.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Providing a seamless and personalized customer experience.
By providing excellent customer service, you can build stronger customer relationships and increase customer loyalty.
Improved Marketing ROI and Reporting
CRM systems provide comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing you to track the performance of your marketing campaigns and measure your ROI. You can track key metrics such as:
- Conversion Rates: Measuring the percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculating the cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Estimating the revenue a customer will generate over their lifetime.
- Campaign Performance: Tracking the performance of individual marketing campaigns.
By analyzing these metrics, you can identify what’s working and what’s not, optimize your campaigns, and improve your overall marketing ROI.
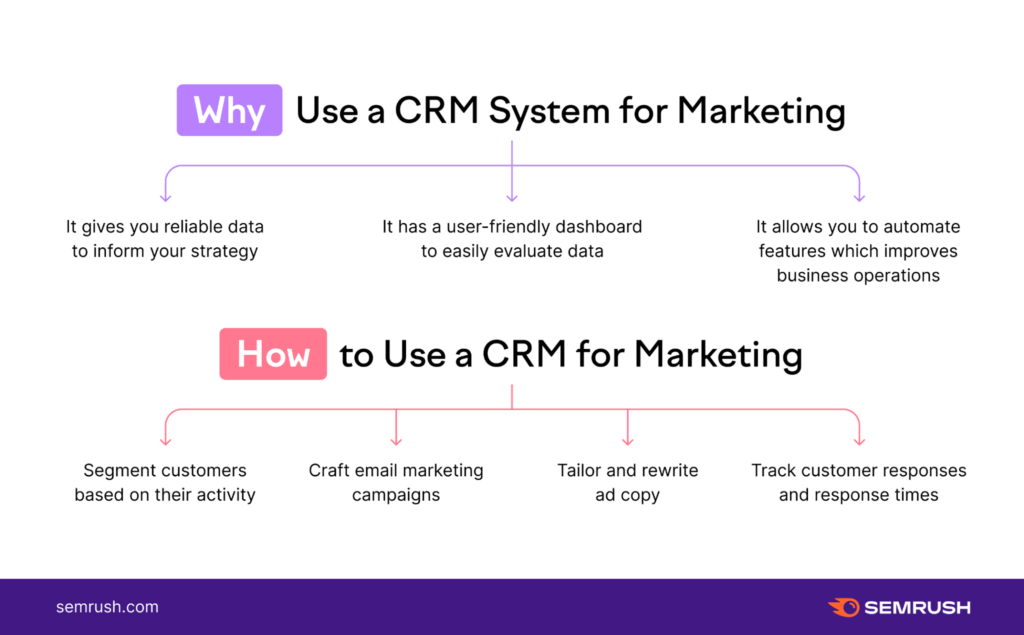
Essential Features of a CRM System for Marketing
To effectively leverage CRM for marketing, you need a system that includes the following essential features:
Contact Management
This is the foundation of any CRM system. It allows you to store and manage all your customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles. It’s the core of your customer database.
Lead Management
Lead management features enable you to capture, track, and nurture leads throughout the sales funnel. This includes lead scoring, automated lead nurturing campaigns, and lead assignment.
Sales Force Automation (SFA)
SFA features automate sales processes, such as opportunity management, quote generation, and order management. This helps your sales team close deals more efficiently.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation features allow you to automate repetitive marketing tasks, such as email marketing, social media posting, and lead nurturing. This saves time and improves efficiency.
Workflow Automation
Workflow automation allows you to automate business processes, such as lead routing, customer service ticket assignment, and sales approvals. This streamlines operations and reduces manual effort.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics features provide you with the data and insights you need to track the performance of your marketing campaigns, measure your ROI, and make informed decisions.
Integration Capabilities
Your CRM system should integrate with other tools and platforms, such as your website, email marketing platform, social media channels, and e-commerce platform. This ensures that data flows seamlessly between your systems.
Implementing a Successful CRM Marketing Strategy
Implementing a successful CRM marketing strategy requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps to follow:
Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before you start, you need to define your goals and objectives. What do you want to achieve with your CRM system? Are you looking to increase sales, improve customer satisfaction, or optimize your marketing ROI? Having clear goals will guide your implementation process.
Choose the Right CRM System
There are many CRM systems available, so it’s important to choose the one that best fits your needs and budget. Consider factors such as:
- Features: Does the system offer the features you need, such as contact management, lead management, marketing automation, and reporting?
- Scalability: Can the system scale to accommodate your future growth?
- Ease of Use: Is the system easy to use and navigate?
- Integration Capabilities: Does the system integrate with your other tools and platforms?
- Pricing: Is the pricing model affordable for your business?
Clean and Organize Your Data
Your CRM system is only as good as the data it contains. Before you start using your CRM, you need to clean and organize your data. This includes:
- Removing duplicate records.
- Correcting inaccurate data.
- Standardizing data formats.
- Segmenting your customer base.
Train Your Team
Training is essential for ensuring that your team knows how to use the CRM system effectively. Provide training on all aspects of the system, including contact management, lead management, sales force automation, and reporting.
Develop a Marketing Automation Strategy
Marketing automation is a key component of a successful CRM strategy. Develop a strategy that outlines how you will use automation to nurture leads, personalize your marketing campaigns, and improve customer engagement.
Measure and Analyze Your Results
Regularly measure and analyze your results to track the performance of your CRM system and marketing campaigns. Use the data to identify areas for improvement and optimize your strategies.
Continuously Optimize
CRM marketing is an ongoing process. Continuously optimize your strategies based on the data you collect and the feedback you receive. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM trends and best practices.
Choosing the Right CRM Software: A Guide
Selecting the right CRM software is a critical decision. The market is awash with options, each boasting different features and functionalities. Here’s a breakdown to help you choose wisely:
Consider Your Business Needs
Before diving into specific software, identify your business’s unique needs. Ask yourself:
- What are my primary goals for implementing a CRM? (e.g., increased sales, improved customer service)
- What are my key marketing processes?
- What size is my business, and how much do I anticipate it growing?
- What specific features are essential for my team?
Answering these questions will help you narrow down your choices and focus on software that aligns with your requirements.
Evaluate Key Features
Different CRM systems offer varying feature sets. Prioritize the features that align with your business needs. Some essential features to consider include:
- Contact Management: Ability to store and manage contact information.
- Lead Management: Tools for capturing, scoring, and nurturing leads.
- Sales Automation: Workflow automation, opportunity management, and sales pipeline tracking.
- Marketing Automation: Email marketing, social media integration, and campaign management.
- Reporting and Analytics: Customizable dashboards and reporting capabilities.
- Integration: Compatibility with other tools you use, such as email marketing platforms, e-commerce systems, and social media channels.
- Mobile Accessibility: Access to CRM data and functionality on mobile devices.
Assess Scalability
Choose a CRM system that can scale with your business. Consider how the software will handle increased data volume, user growth, and evolving business processes. Look for systems that offer flexible pricing plans and the ability to add features as your needs change.
Consider User-Friendliness
A CRM system is only effective if your team uses it. Choose a system with an intuitive interface and user-friendly design. Look for systems that offer training resources, tutorials, and responsive customer support.
Evaluate Pricing and Implementation Costs
CRM software pricing models vary. Some systems offer subscription-based pricing, while others offer one-time licensing fees. Consider the total cost of ownership, including implementation costs, training, and ongoing maintenance. Compare pricing plans and features to find the best value for your budget.
Research Reviews and Case Studies
Before making a decision, research reviews and case studies of different CRM systems. Read what other businesses have to say about their experiences. Look for systems that have a proven track record of success and positive customer feedback.
Consider Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are crucial considerations. Choose a CRM system that offers robust security features, such as data encryption, access controls, and regular backups. Ensure that the system complies with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Best Practices for CRM Marketing Performance
Implementing a CRM system is just the first step. To maximize your CRM marketing performance, follow these best practices:
Data Quality is King
Your CRM system is only as good as the data it contains. Invest time and effort in ensuring your data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. Regularly clean and update your data to remove duplicates, correct errors, and ensure consistency.
Focus on the Customer Journey
Map out your customer journey and identify all the touchpoints where you interact with your customers. Use your CRM to personalize the customer experience at each touchpoint. Tailor your messaging, offers, and content to the customer’s stage in the journey.
Embrace Automation Wisely
Marketing automation can save you time and improve efficiency. However, don’t automate everything. Use automation to streamline repetitive tasks, but always maintain a human touch. Personalize your automated communications to make them feel more relevant and engaging.
Integrate CRM with Other Tools
Integrate your CRM system with other tools and platforms you use, such as your website, email marketing platform, social media channels, and e-commerce platform. This ensures that data flows seamlessly between your systems and provides a 360-degree view of your customers.
Test and Optimize Continuously
Test different marketing campaigns and strategies to see what works best. Use A/B testing to compare different versions of your emails, landing pages, and offers. Continuously analyze your results and optimize your strategies to improve your performance.
Foster Collaboration
Encourage collaboration between your marketing, sales, and customer service teams. Share data and insights to ensure that everyone is aligned on your customer strategy. Use your CRM to facilitate communication and collaboration.
Prioritize Mobile Access
Make sure your CRM system is accessible on mobile devices. This allows your team to access customer data and manage customer interactions on the go. Consider mobile-friendly CRM apps or responsive web design.
Provide Ongoing Training
Provide ongoing training to your team on how to use the CRM system effectively. Stay up-to-date on the latest CRM features and best practices. Regularly review your CRM processes and identify areas for improvement.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While CRM offers immense potential, businesses often face challenges. Being aware of these challenges and having strategies to address them is crucial for success:
Data Quality Issues
Challenge: Inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated data can undermine the effectiveness of your CRM system. Garbage in, garbage out.
Solution: Implement data cleansing processes. Regularly review and update data. Use data validation rules to ensure data accuracy. Consider using third-party data enrichment services.
Lack of User Adoption
Challenge: If your team doesn’t use the CRM system, you won’t reap the benefits. Resistance to change or lack of understanding can hinder adoption.
Solution: Provide adequate training and support. Make the system easy to use. Demonstrate the value of the CRM to your team. Involve users in the implementation process. Celebrate successes and provide ongoing feedback.
Integration Problems
Challenge: Difficulty integrating your CRM with other systems can limit its functionality and create data silos.
Solution: Choose a CRM system that integrates seamlessly with your other tools. Plan your integration strategy carefully. Test the integrations thoroughly. Seek help from a CRM consultant if needed.
Poorly Defined Processes
Challenge: Without clear processes, your CRM system will be inefficient and ineffective.
Solution: Define clear sales, marketing, and customer service processes. Document your processes. Automate your processes where possible. Regularly review and refine your processes.
Lack of Executive Support
Challenge: Without strong leadership support, it’s difficult to implement and maintain a successful CRM strategy.
Solution: Secure buy-in from your executive team. Communicate the value of the CRM to leadership. Regularly report on the results of your CRM efforts.
The Future of CRM Marketing
The landscape of CRM marketing is constantly evolving. Here’s a glimpse into the future:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming CRM. AI-powered CRM systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict customer behavior, and automate tasks. Expect to see more AI-driven personalization, predictive analytics, and automated customer service.
Hyper-Personalization
Customers expect personalized experiences. CRM systems will leverage data to provide even more personalized experiences, including personalized product recommendations, tailored content, and customized offers.
Omnichannel Marketing
Customers interact with businesses across multiple channels. CRM systems will enable businesses to provide seamless, consistent experiences across all channels, including email, social media, website, and mobile apps.
Focus on Customer Experience (CX)
Customer experience will be the driving force behind CRM strategies. Businesses will prioritize providing exceptional customer experiences at every touchpoint. CRM systems will play a critical role in enabling these experiences.
Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security will become even more important. CRM systems will need to comply with evolving data privacy regulations. Businesses will need to prioritize data security to protect customer information.
Conclusion: The Power of CRM for Marketing Performance
CRM is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses that want to thrive in today’s competitive market. By implementing a well-executed CRM strategy, you can gain a deep understanding of your customers, personalize your marketing campaigns, improve customer experience, increase sales and revenue, and optimize your marketing ROI. By embracing the best practices outlined in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of CRM and drive sustainable growth for your business. The journey to CRM success requires commitment, planning, and a customer-centric approach. Embrace the power of CRM, and watch your marketing performance soar.